Four security updates to get ahead of proposed 2025 HIPAA amendments
A new set of 2025 HIPAA security updates are on the horizon, bringing significant changes that aim to bolster the protection of electronic protected health information (ePHI). As cyber threats intensify, these updates are more than just regulatory formalities; they are critical measures to safeguard sensitive data.
Published in early January, the 2025 HIPAA Security Amendments are set to significantly enhance the protection of ePHI. The proposed changes are based off the US Department of Health and Human Services’ (HHS) goals of both addressing changes in the health care environment and clarifying what compliance obligations look like for regulated entities.
Organizations have 180 days to reach compliance according to stricter standards of identity cybersecurity if the proposed updates pass.
In order to be prepared, here are four things your organization or managed security service provider should focus on:
Deployment of mandatory security controls
Securing against known vulnerabilities
Documentation for annual audits
Clear goals for visibility, prevention, and remediation
But first, a quick recap of how the standard has evolved.
Background on the HIPAA Security Rule
The last major revision of the HIPAA Security Rule dates back to 2013 and the “Omnibus HIPAA Final Rule,” introduced to strengthen patient privacy and security protections. Amongst other requirements, the HIPAA Omnibus Rule of 2013 made business associates of covered entities directly liable for HIPAA compliance and adopted a four-tiered civil monetary penalty structure for violations that bumped the maximum fine from $25,000 per year to up to $1.5 million. That is to say, healthcare organizations and business partners may face greater liability in case of a security breach.
Between 2022 and 2023, the HIPAA Journal reported a jump from 51.9 million to 168 million records impermissibly disclosed. In 2024, the average data breach size jumped from 225,000 to nearly 400,000, though reports are still being counted. These alarming statistics underscore an urgent need for an amendment that encourages more stringent security measures to protect patient information.
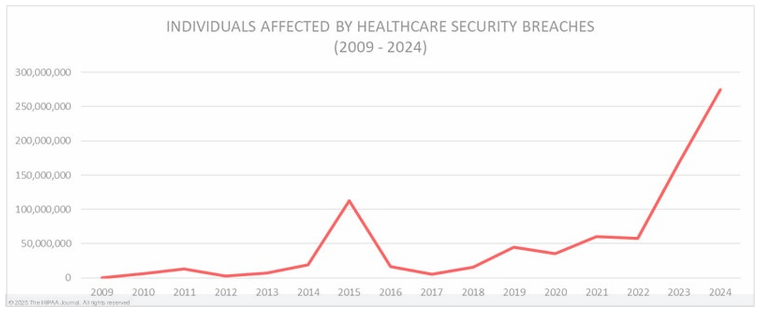
Imaged sourced from HIPAA Journal, January 20, 2025
Key proposed changes to HIPAA Security Rule in 2025
1. Deploy mandatory security controls, such as MFA
"[The Department] provides that MFA as a source of identity and access security control is an important means to control access to infrastructure and conduct proper change management control." — HIPAA Security Rule To Strengthen the Cybersecurity of Electronic Protected Health Information, 2025, p. 87
The implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) is no longer optional. While the current Secure Rule allows distinction between “required” and “addressable” implementation specifications, the 2025 update makes all implementation specifications required with only specific, limited exceptions. That makes deploying security controls like MFA to all users essential for reducing unauthorized access risks.
In the proposal, regulated entities would be required to apply the proposed rule’s specific requirements for authenticating users’ identities through verification of at least two of three categories of factors of information about the user:
Information known by the user, including but not limited to a password or personal identification number (PIN).
Item possessed by the user, including but not limited to a token or a smart identification card.
Personal characteristic of the user, including but not limited to fingerprint, facial recognition, gait, typing cadence, or other biometric or behavioral characteristics.
Cisco Duo’s award-winning MFA strengthens access control, providing an additional layer of security that is crucial for protecting PHI without adding unnecessary friction for busy end-users and health practitioners. Importantly, it protects against advancing identity-based attacks by offering wide coverage of authenticators—and the option to intelligently “step-up” login security according to detected risk patterns and access behaviors.
With the widest range of supported authenticators, Duo helps organizations transition away from weaker SMS and phone-call 2FA and towards push-based smartphone apps with verified number matching and phishing-resistant or passwordless authenticators.
Learn more about the types of Duo authenticators available.
2. Defining and preparing against known vulnerabilities
With the proposed amendment, organizations must now identify potential threats and vulnerabilities with greater accuracy, and with increased frequency at least once every six months (p.385). This includes insights across the supply chain, including external contractors and any partners who may have access to ePHI.
The Department also specifically updated the Security Role to define vulnerability, identifying that: “...exploitable vulnerabilities exist across many components of IT infrastructures including, but not limited to, servers, desktops, mobile device operating systems, web software, and firewalls” (p. 99).
In addition, HHS recommended that regulated entities “install vendor patches, make software updates, and monitor sources of cybersecurity alerts describing new vulnerabilities,” (p. 99) citing the NIST National Vulnerability Database and CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog.
Outdated software and operating systems pose common challenges for organizations looking to improve security—especially in a field like healthcare with several types of devices and legacy applications. One option is to install device managers like Cisco Meraki, Jamf, or Intune onto endpoints to enforce updates. However, for healthcare practices with contractors, unmanaged and BYOD devices, or simply desiring a less-invasive option, the management and maintenance of vulnerability patching can quickly become an IT strain.
Duo’s agent-free approach enforces device trust is at every point of authentication, checking for OS patches, firewall, encryption, and other security policies before granting access into sensitive ePHI. Without heavy, permission-demanding clients to install, Duo Desktop verifies the health and security of endpoint devices. The Duo Authenticator app also picks up on mobile device telemetry like if a device is running the latest OS patch, has full disk encryption enabled, and whether the device is jailbroken or rooted.
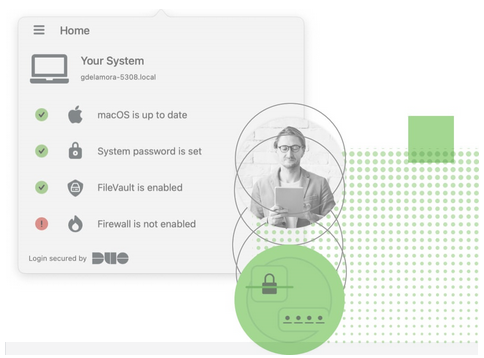
A lightweight client application for macOS, Windows, and Linux, Duo Desktop checks for device vulnerabilities before granting access. Available in Duo Advantage and Premier editions.
Duo analyzes what’s running on all users’ devices—managed or unmanaged, without the use of an agent. With data in an actionable device health report, administrators can easily see:
An analysis of users’ devices, including current device OS, browsers, Flash and Java versions.
Security health trends of all devices accessing business applications, including which devices are outdated or need to be updated by end users.
The latest security events that may result in outdated devices, including a new browser or plugin update released by a software vendor.
Rather than pushing an update to the device, Duo encourages end-users to self-remediate out-of-date endpoints by only allowing access to protected applications if the device passes an organization’s configurable policies. This also cuts down on costly and unnecessary helpdesk and IT costs.
3. Have documentation for annual audits
Annual audits will now be a requirement for ensuring ongoing compliance according to proposed updates.
While the Security Rule does not currently require regulated entities to conduct internal or third-party compliance audits, such activities are important components of a robust cybersecurity program. Cybersecurity audits for insurance and regulatory bodies typically request paper trails documenting users, the applications they access, and the devices they’re accessing resources from. This can be challenging to deliver on—especially for supply chain partners or contractors with unmanaged devices.
Duo’s identity security solution provides complete device visibility into both managed and unmanaged devices. With Duo, you can maintain an inventory of all trusted devices accessing corporate resources, identify at-risk devices, and gain a deeper understanding of your security environment. This not only helps in preparing for audits, but more importantly continuously reduces risk by verifying trust of users, patching device vulnerabilities, and minimizing instances of shadow IT.
Duo’s dashboard provides security administrators with a snapshot of the overall access activity across their organization. The Duo Admin Panel simplifies ongoing compliance processes with comprehensive audit logs and reports for all users, applications, devices, and associated authentication behaviors, facilitating easier audit preparation and certification. Admins get timely lists of access attempts and the MFA protections in place for a specific user. They can also identify how many accessing devices have out-of-date operating systems and enable self-remediation.
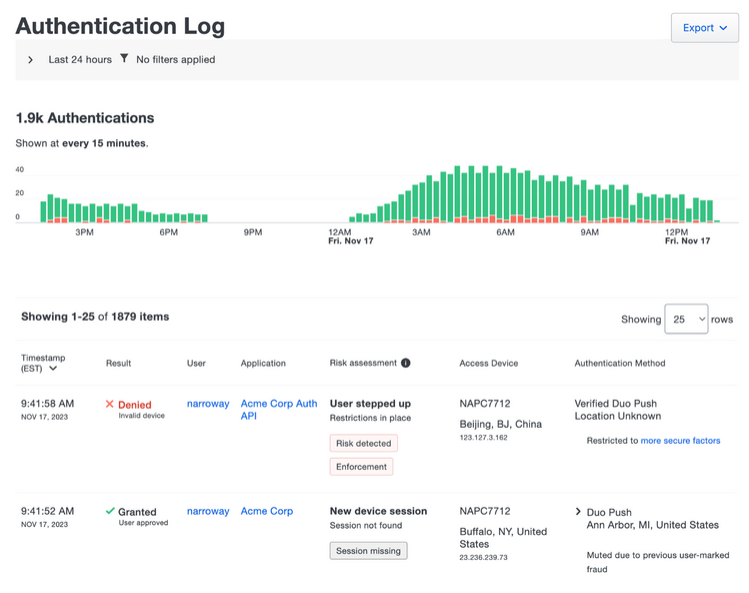
"The dashboard gives us a high-level view of our organization. Useful information such as login failures, who logged into which application and when, number of deployed licenses and inactive users are all available right there. I can then easily drill down to the details of a specific login event with just a few clicks. We did not have this level of information before Duo." — Security Architect, on how Duo helps to meet compliance and protect private patient information for a major healthcare provider in the Pacific Northwest. Read the full case study
4. A focus on visibility, prevention, and remediation
It’s clear that identity security will be a growing priority in 2025, especially with 80% of breaches leveraging identity as a key component according to Cisco Talos incident response reporting. Having complete visibility across an organization’s entire user environment is essential to reducing the risk of compromised credentials or other vulnerabilities—and a helpful tool for generating security reports.
With a complete view of your entire user inventory—including employees, contractors, and vendors—you can significantly reduce the risk of a breach and protect sensitive PHI data. Duo and Cisco Identity Intelligence pool insights across identity providers and storages, which make it easy to clean up dormant accounts, expand multi-factor authentication usage, and reduce administrator privilege creep. It also enables continuous status checks on the compliance requirements that are important to the industry.
Cisco Identity Intelligence adds a comprehensive layer of visibility, detection, and remediation that defends against security vulnerabilities outlined by HHS:
Filter for users and identities that do not have MFA configured across all storage locations and MFA providers
Get detailed insights on the devices accessing organization resources on a per-user basis, and set alerts for critical resources
Run security checks that search for known vulnerabilities and align to security frameworks including MITRE ATT&CK, NIST, and CIS
Generate reports on common audit requirements like MFA enrollment, license utilization, device operating system information, and shared accounts
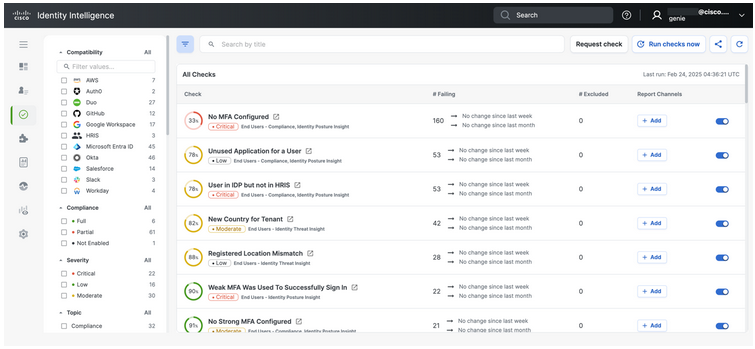
A view of the checks performed by Cisco Identity Intelligence across all identity storages. Set up automated alerts for your organization’s security priorities, including checks aligned to industry and compliance frameworks. Identity Intelligence is available with the Duo Advantage and Premier editions.
The financial implications of these changes are significant, with estimated costs of $9 billion in the first year according to the Department of Health and Human Services (p. 302). However, the cost of inaction—potential data breaches, compromised patient safety, and legal repercussions—could be far greater. The Security Rule updates are not just about compliance; they are about safeguarding critical infrastructure and patient data, so visibility is key.
Take identity security to the next level with Duo
"The HHS 405(d) Program’s ‘Health Industry Cybersecurity Practices: Managing Threats and Protecting Patients’ recommends a <strong>layered approach to cyber defense</strong> (i.e., if a first layer is breached, a second exists to prevent a complete breach)." — HIPAA Security Rule To Strengthen the Cybersecurity of Electronic Protected Health Information, 2025, p. 86
The 2025 HIPAA Security Updates mark a significant shift in healthcare security practices. While MFA is a powerful tool that offers significant benefits in protecting PHI, it is no longer sufficient for the fight against unauthorized access. Identity security features like Duo’s device trust and adaptive authentication establish additional layers of security that both protect ePHI and defend organizational liability. For example, the ability to enforce security posture on the devices accessing sensitive patient health information with system reporting can help provide evidence of device encryption if equipment is lost or stolen.
Organizations that achieve compliance avoid audit penalties and enhance their overall security posture for future requirements. Duo’s easy-to-use interface and clear pricing reduces the TCO associated with traditional security tools like hardware tokens as well as deployment costs and undue burdens on IT teams.
Duo helps protect confidential patient information by integrating with Epic’s EHR to provide secure remote access that’s tailored to the needs of the healthcare industry. Duo supports Epic's newest Hyperdrive e-prescription workflow and continues to support the original Hyperspace workflow.
When it comes to the go-live of this specific Security Rule update, stakeholders have a 60-day window to submit comments on the proposal. In the meantime, healthcare organizations should begin reviewing their security programs internally or with their security providers and prepare for upcoming changes.
For a fact sheet on the new HIPAA Updates, visit the HHS website.
For more details on why Duo for Healthcare, visit the Healthcare solutions page.
If you’re a managed service provider looking to become a Duo partner, visit the Duo MSP page.

