Duo Authentication for Windows Logon and RDP
Last updated:
WARNING: An issue is present in the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon 5.2.0 installer which may cause removal of Duo registry keys and values created after the initial installation when upgrading from a prior version to 5.2.0 using a silent install method. This affects existing user offline access and paswordless OS logon enrollments and users may need to re-enroll in offline access and passwordless OS logon.
This issue is not seen with interactive GUI installations and is corrected in the 5.2.1 release. Please do not install 5.2.0 via silent install if any user enrollments in offline access or passwordless OS logon, or any Duo registry keys and values created after your initial install exist on your clients.
Learn more about the 5.2.0 installer issue in the article Guide to issues with the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon 5.2.0 installer in the Duo Knowledge Base.
Overview
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon adds Duo two-factor authentication to these Windows and Windows Server logon scenarios:
- Local or domain account logins
- Logins at the local console and/or incoming Remote Desktop (RDP) connections
- Credentialed User Access Control (UAC) elevation requests (e.g. Right-click + "Run as administrator") in v4.1.0 and later
Duo's Windows Logon client does not add a secondary authentication prompt to the following logon types:
- Shift + right-click "Run as different user"
- PowerShell "Enter-PSSession" or "Invoke-Command" cmdlets
- Non-interactive logons (i.e. Log on as a Service, Log on as Batch, Scheduled Tasks, drive mappings, etc.)
- Pre-Logon Access Providers (PLAPs) such as Windows Always On VPN
- RDP Restricted Admin Mode
Duo Premier and Advantage plan customers can protect PowerShell and SSH with Duo Windows Command Line Protection.
Important Notes
Please review all these compatibility and installation notes before proceeding.
- Installing Duo Authentication for Windows Logon adds two-factor authentication to all interactive user Windows login attempts, whether via a local console or over RDP, unless you select the "Only prompt for Duo authentication when logging in via RDP" option in the installer. If two-factor is enabled for both RDP and console logons, it may be bypassed by restarting Windows into Safe Mode (e.g. in case of a configuration error). If you wish to protect local console logons with Duo, please see the FAQ for some guidance on securing your Windows installation appropriately.
- Additional configuration may be required to log in using a Microsoft attached account. See Can I Use Duo with a Microsoft Account? for more information.
- Windows users must have passwords to log in to the computer. Users with blank passwords may not login after Duo Authentication installation.
- It's a good idea to have your BitLocker recovery key available in the event you need to boot into safe mode to uninstall Duo.
- Review these Duo Knowledge Base articles for additional security recommendations:
- Duo application features like failmode, offline access, and UAC protection may be configured during installation or post-installation via Regedit or Group Policy. Please see our FAQ for more information.
This application communicates with Duo's service on SSL TCP port 443.
Firewall configurations that restrict outbound access to Duo's service with rules using destination IP addresses or IP address ranges aren't recommended, since these may change over time to maintain our service's high availability. If your organization requires IP-based rules, please review Duo Knowledge Base article 1337.
Effective June 30, 2023, Duo no longer supports TLS 1.0 or 1.1 connections or insecure TLS/SSL cipher suites. See Duo Knowledge Base article 7546 for additional guidance.
TLS Requirements
Effective June 30, 2023, Duo no longer supports TLS 1.0 or 1.1 connections or insecure TLS/SSL cipher suites.
The current version of Duo for Windows Authentication supports TLS 1.2 when installed on a version of Windows that also supports and uses TLS 1.2 or higher.
See the article Guide to TLS support for Duo applications and TLS 1.0 and 1.1 end of support for more information.
System Requirements
Windows Versions
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon supports both client and server operating systems.
Clients:
- Windows 10 (as of v1.1.8)
- Windows 11 (as of v4.2.0)
Servers (GUI installs only as of v4.0.0):
- Windows Server 2016 (as of v2.1.0)
- Windows Server 2019 (as of v4.0.0)
- Windows Server 2022 (as of v4.2.0)
- Windows Server 2025 (as of v5.0.0)
Ensure your system's time is correct before installing Duo.
System Processor
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon supports devices with ARM64 processors, like the Surface Pro X, as of version 5.2.0. ARM64 devices must run Windows 10 version 1709 or later.
Visual C++ Redistributable
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon 4.3.16 and later depend on the Microsoft Visual C++ 2022 Redistributable. The Duo EXE installer (i.e. duo-win-login-5.2.1.exe) will also install the Visual C++ Redistributable package on your system if a compatible version is not already present.
Duo Factor Support
Duo for Windows Logon supports these factor types for online two-factor authentication:
- Duo Push (Duo Mobile)
- Duo Verified Push (as of v4.3.16)
- Duo Mobile Passcodes
- SMS Passcodes
- Hardware Token OTP passcodes (including Yubikey OTP)
- Phone Call
- Bypass Codes
U2F security key support is limited to Offline Access only.
Enroll Users Before Installation
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon doesn't support inline self-service enrollment for new Duo users.
Unenrolled users, that is, users that do not yet exist in Duo with an attached 2FA device, must be created manually by an administrator, imported by an administrator or self-enrolled through Duo Central or another application which supports Duo’s self-service enrollment (see Test Your Setup) before those users can log in with Duo for Windows Logon.
The Duo username (or username alias) should match the Windows username. When you create your new RDP application in Duo the username normalization setting defaults to "Simple", which means that the if the application sends the usernames "jsmith," "DOMAIN\jsmith," and "jsmith@domain.com" to Duo at login these would all resolve to a single "jsmith" Duo user.
Duo for Windows Logon supports Duo Push, phone callback or SMS passcodes, and passcodes generated by Duo Mobile or a hardware token as authentication methods. Duo users must have one of these methods available to complete 2FA authentication.
If the user logging in to Windows after Duo installation does not exist in Duo, the user may not be able to log in to the system.
Read the enrollment documentation to learn more about enrolling your users in Duo.
See the Deployment Tip below to learn how you can use the New User Policy to deploy Duo for Windows Logon without enrolling your users first or requiring Duo authentication immediately after installation.
First Steps
Before moving on to the deployment steps, it's a good idea to familiarize yourself with Duo administration concepts and features like options for applications, available methods for enrolling Duo users, and Duo policy settings and how to apply them. See all Duo Administrator documentation.
-
Log in to the Duo Admin Panel and navigate to Applications → Application Catalog.
-
Locate the entry for Microsoft RDP with the "2FA" label in the catalog. Click the + Add button to create the application and get your integration key, secret key, and API hostname. You'll need this information to complete your setup. See Protecting Applications for more information about protecting applications with Duo and additional application options.
-
No active Duo users can log in to new applications until you grant access. Update the User access setting to grant access to this application to users in selected Duo groups, or to all users. Learn more about user access to applications. If you do not change this setting now, be sure to update it so that your test user has access before you test your setup.
This setting only applies to users who exist in Duo with "Active" status. This does not affect application access for existing users with "Bypass" status, existing users for whom the effective Authentication Policy for the application specifies "Bypass 2FA" or "Skip MFA", or users who do not exist in Duo when the effective New User Policy for the application allows access to users unknown to Duo without MFA. -
We recommend setting the New User Policy for your Microsoft RDP application to Deny Access, because no unenrolled user may complete Duo enrollment via this application.
-
If you'd like to enable Passwordless Operating System (OS) logon to Windows you can do that now in the "Passwordless Settings" section of the Duo application page, or return to the Admin Panel later to configure Passwordless OS Login after first verifying logon success with username, password, and two-factor authentication.
-
If you'd like to enable offline access with Duo MFA you can do that now in the "Offline Access Settings" section of the Duo application page, or return to the Admin Panel later to configure offline access after first verifying logon success with two-factor authentication.
-
Download the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installer package. View checksums for Duo downloads here.
The security of your Duo application is tied to the security of your secret key (skey). Secure it as you would any sensitive credential. Don't share it with unauthorized individuals or email it to anyone under any circumstances!
Verified Duo Push for Windows Logon
Available in: Duo Essentials, Duo Advantage, and Duo Premier
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 4.3.16 and later supports Verified Duo Push with a numeric code. As 4.3.16 was a beta Duo release, we recommend updating systems to version 5.0.0 or later. In addition, Verified Duo Push requires Duo Mobile 4.16.0 or later on Android 8+ or Duo Mobile 4.17.0 or later on iOS 16+, activated for Duo Push.
Applying an Authentication Methods policy enabling Verified Duo Push with a verification code to a Microsoft RDP Duo application will require users to enter the verification code during Windows logon into the Duo Mobile app when performing a Duo Push to authenticate.
Do not apply a policy to your Microsoft RDP Duo application enabling either of the following authentication methods:
These methods do not work with Duo Authentication for Windows Logon and can block your users from authenticating.
To enable Verified Duo Push for Windows Logon:
-
Create a new custom policy or update an existing policy which enables both the Require Verified Duo Push and Require users to enter a verification code options in the Authentication Methods policy settings. Click Save Policy when done.
-
Apply the custom policy to your Microsoft RDP Duo application as a group or application policy. If you made the change in your global policy then the setting applies to all your Microsoft RDP Duo applications.
The policy setting takes immediate effect — there is no need to reinstall Duo Authentication for Windows Logon as long as clients have already installed v4.3.16 or later. Systems with older versions of Duo for Windows Logon will continue offering the standard Duo Push experience and must upgrade to a supported release. to use Verified Duo Push.
With this policy setting applied, users must enter the verification code shown on the Duo for Windows Logon prompt into the Duo Mobile authentication request.
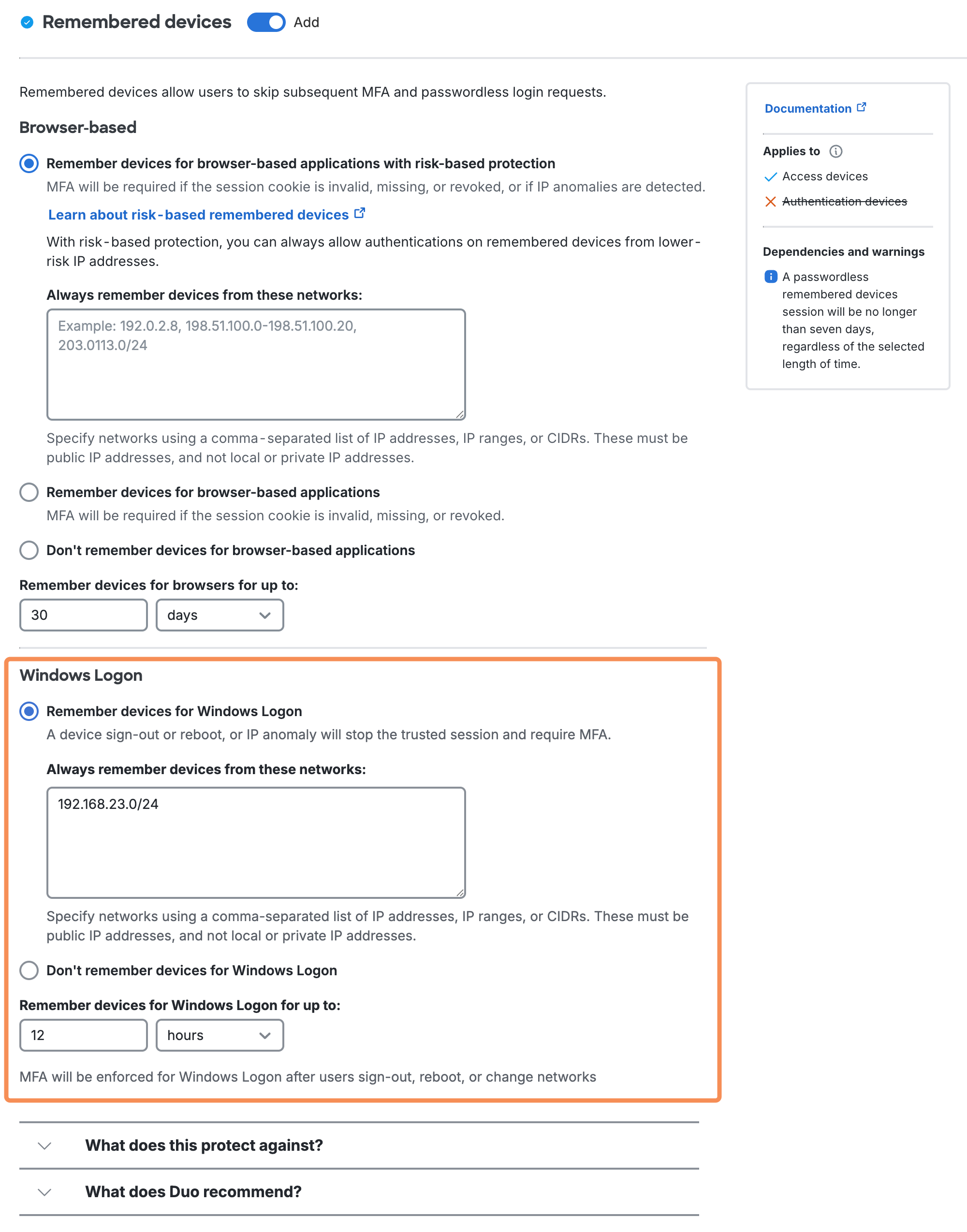
Remembered Devices for Windows Logon
Available in: Duo Essentials, Duo Advantage, and Duo Premier
Version 4.2.0 of Duo Authentication for Windows Logon adds support for local trusted sessions, reducing how often users must repeat Duo two-factor authentication. The Remembered Devices policy now includes a setting for Windows logon sessions, which when enabled offers users a "Remember me" checkbox during local console login for the duration specified in the policy.
When users check this box and complete Duo authentication, they aren't prompted for Duo secondary authentication when they unlock the workstation after that initial authentication until the configured trusted session time expires. Duo for Windows Logon invalidates the current trusted session and the next Windows logon or unlock attempt will require Duo authentication again if any of the following occurs:
- An administrator resets the user's remembered devices session in the Duo Admin Panel.
- The user changes networks and the effective policy doesn't include the new network.
- The user authenticates with offline access while the workstation is disconnected.
- The user logs out of Windows.
- The user reboots the workstation.
- The user clicks the "Cancel" button in the Duo authentication prompt during workstation unlock.
To enable remembered devices for Windows Logon:
-
Create a new custom policy or update an existing policy for remembered devices which enables the Remember devices for Windows Logon option, and enter the number of hours or days you want a trusted Windows logon session to last.
Client network changes, such as moving between WiFi networks, invalidate a Windows logon remembered devices session. You can allow persistent remembered devices sessions across trusted networks by entering network IPs, IP ranges, or CIDRs under Always remember devices from these networks. Duo Authentication for Windows Logon 5.2.0 and later will not invalidate a remembered devices session as long as the client is authenticating from a network you specify here.
Click Save Policy when done.
-
Apply the custom policy to your Microsoft RDP Duo application as a user-group or application policy. If you made the change in your global policy then the setting applies to all your Microsoft RDP Duo applications, unless any of them have a policy assigned with conflicting remembered Windows Logon device settings.
The policy setting takes immediate effect — there is no need to reinstall the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon application after updating the remembered device policy as long as clients have already installed v4.2.0 or later. Systems with older versions of Duo for Windows Logon must upgrade to 4.2.0 or later to see the new option.
With this policy setting applied, users who log on to the local Windows console see an additional option on the Duo for Windows Logon prompt for remembering the device. This option will not display for RDP/remote logins to Windows systems with Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installed, regardless of the effective remembered devices policy setting for Windows Logon.
Administrators may revoke the Windows local trusted Duo session by unassigning a remembered devices policy for Windows Logon from a Microsoft RDP application, editing the policy attached to a Microsoft RDP application to disable the Windows Logon remembered devices setting, or by deleting the registry entry for the user session from the Windows client. Learn more about this in the Windows Logon FAQ.
Duo Passport and Windows Logon
Duo Passport lets you simplify application access by sharing authenticated sessions between Windows and Duo-protected browser and thick client applications when you have enabled remembered devices in your effective policies. Learn how to configure and enable Duo Passport.
Deployment Tip
To test Duo on your Windows system with a group of pilot users, we suggest setting your application's New User Policy to "Allow Access" while testing. The pilot users that you've enrolled in Duo with an associated 2FA device get prompted to complete Duo authentication, while all other users will be transparently let through.
If you want to deploy Duo to your Windows systems but have no users complete 2FA until a specific date (after all user enrollment is complete), set the New User Policy to "Allow Access" and set the Authentication Policy to "Bypass 2FA". With these two policy settings in place users who have and who have not enrolled in Duo log in to the Windows system as usual without experiencing Duo.
If you chose to enable offline access on your application, then enrolled users who bypass 2FA due to the effective Authentication Policy would still be prompted to complete offline enrollment. To avoid confusion, we recommend leaving offline access off until you require users to complete Duo 2FA while online.
When you're ready to require Duo authentication for all users of the target Windows system, change the "New User Policy" to "Deny access" and change the "Authentication Policy" to "Enforce MFA". This will prompt all enrolled users to perform Duo 2FA after they type in their usernames and passwords, and prevent users who have not enrolled in Duo from logging in without 2FA.
Run the Installer
Installing Duo may require a reboot. Schedule your Duo installation during a maintenance window if unplanned system restarts is a concern.
-
Run the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installer with administrative privileges.
If you receive an "Installation stopped" error from the Duo installer please refer to Duo KB article 6462 for remediation steps.
-
When prompted, enter your API Hostname from the Microsoft RDP application's details page in the Duo Admin Panel and click Next. The installer verifies that your Windows system has connectivity to the Duo service before proceeding.
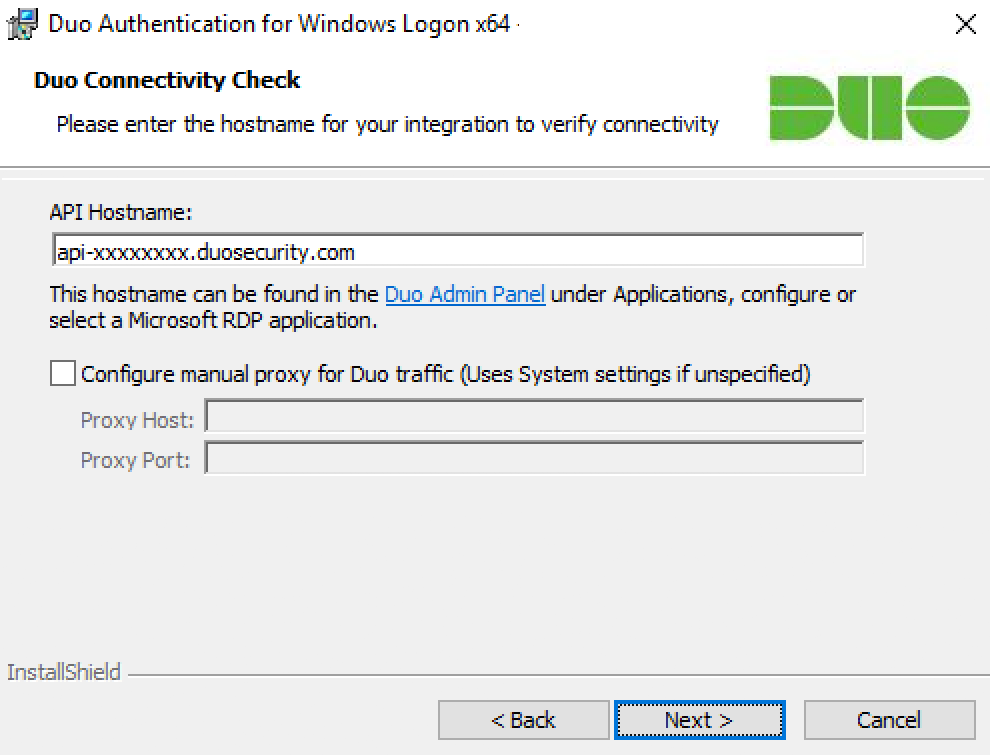
If the connectivity check fails, ensure that your Windows system is able to communicate with your Duo API hostname over HTTPS (port 443).
If you need to use an outbound HTTP proxy in order to contact Duo Security's service, enable the Configure manual proxy for Duo traffic option and specify the proxy server's hostname or IP address and port here.
-
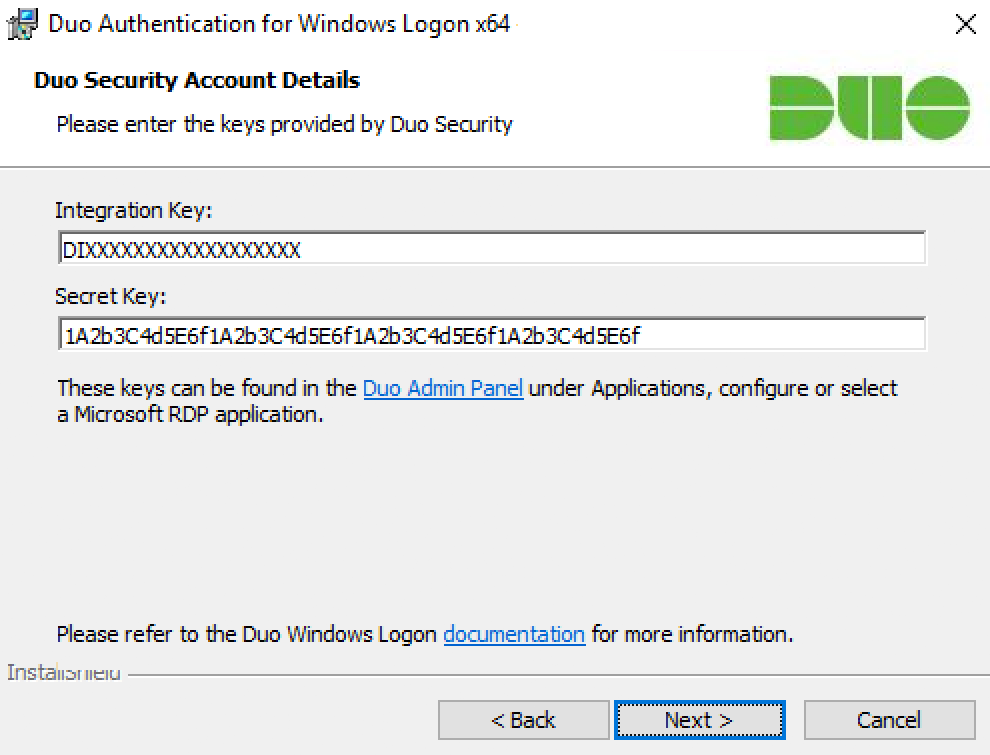
Enter your integration key and secret key from the Microsoft RDP application in the Duo Admin Panel and click Next again.
-
Select your integration options:
Setting Description Bypass Duo authentication when offline (FailOpen) Enable this option to allow user logon without completing two-factor authentication if the Duo Security cloud service is unreachable. If you plan to enable offline access with MFA consider disabling FailOpen.
Windows Logon 4.2.2 and earlier installers enable this setting by default. Windows Logon 4.3.0 installers default to fail closed. The
msiinstaller will preserve the selection made by a previously installed version on upgrade. Upgrades from previous versions using theexeinstaller will override the previous fail mode selection and default to fail closed.Use auto push to authenticate if available Automatically send a Duo Push or phone call authentication request after primary credential validation to the first capable device attached to the user. Checked by default and applies to all users of the target system. Only prompt for Duo authentication when logging in via RDP Leave this option unchecked to require Duo two-factor authentication for console and RDP sessions. If enabled, console logons do not require 2FA approval. If you want to enforce protected offline access to laptop logins, be sure you don’t check this box. If you do, laptop console logins won’t require any form of Duo MFA. 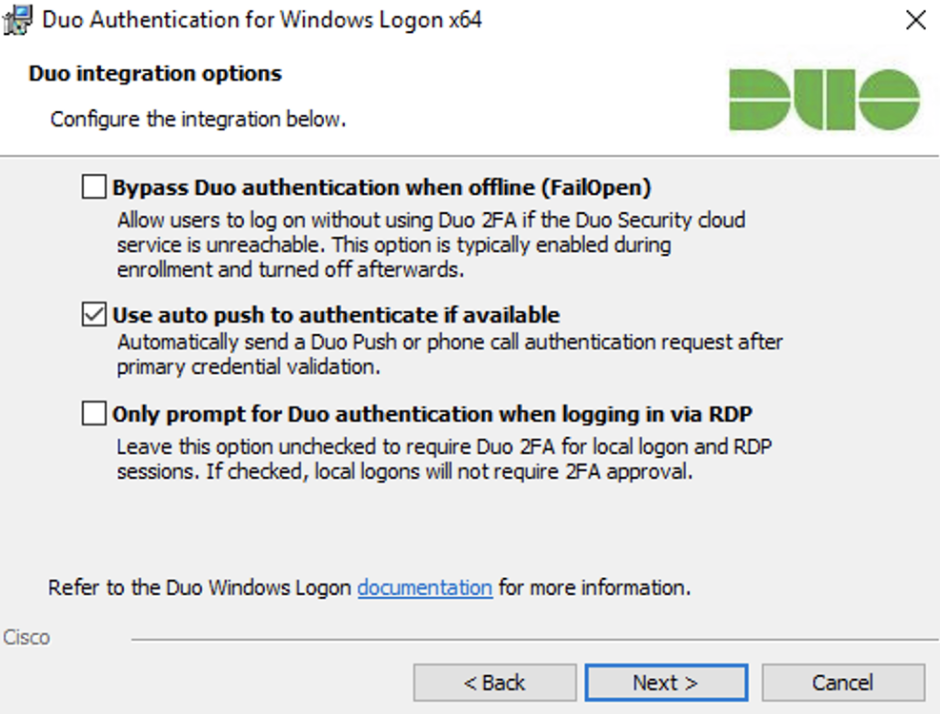
-
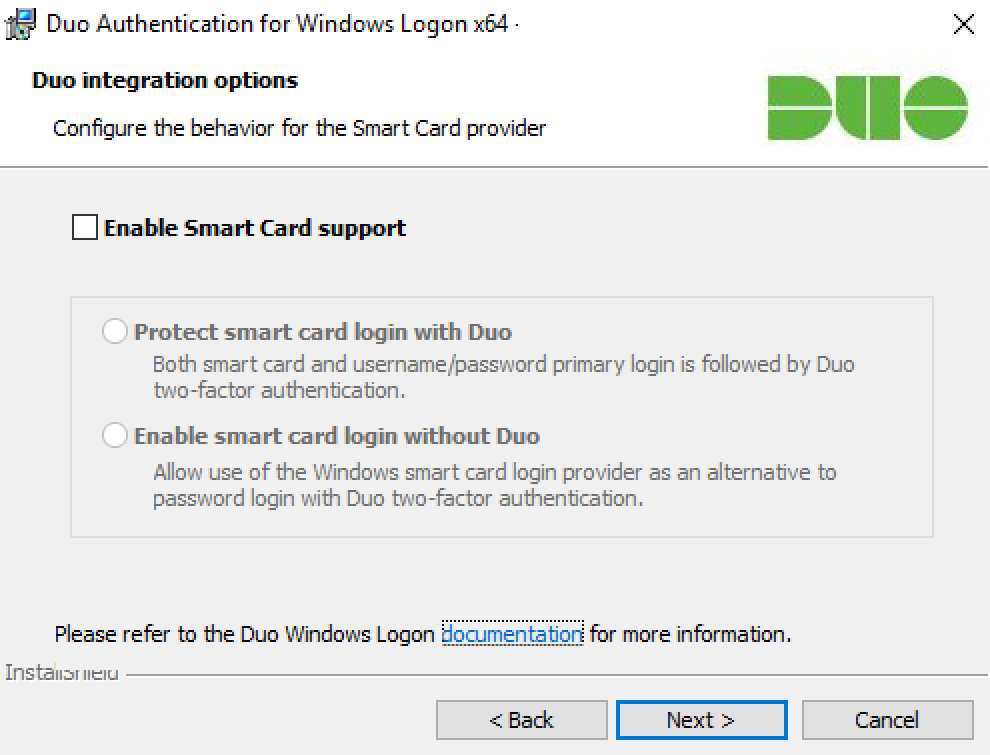
If you plan to use smart cards on the systems where you install Duo, click to Enable Smart Card Support and select your smart card options:
Setting Description Protect smart card login with Duo Select this option to require Duo authentication after primary login with username and password or primary authentication with a smart card. Supported for local console logins. Enable smart card login without Duo Select this option to permit use of the Windows smart card login provider as an alternative to Duo authentication. Smart card logins won't require 2FA. These options only support the Windows native smart card provider. Available in version 3.1.1 and later.
-
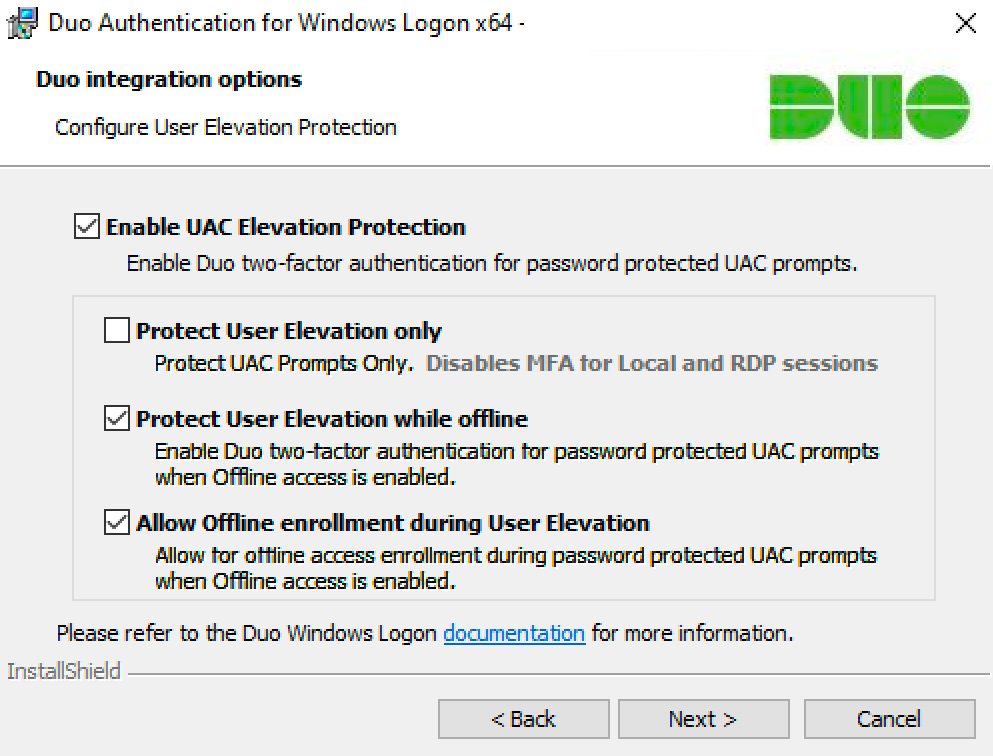
If you'd like to add Duo 2FA protection to account elevation via Windows User Account Control (UAC), click to Enable UAC Elevation Protection and select your elevation options:
Setting Description Protect User Elevation only Enable Duo two-factor authentication at password-protected UAC prompts only. If you check this box Duo will not prompt for 2FA at local or RDP login or workstation unlock. Protect User Elevation while offline Permit offline access authentication for password-protected UAC prompts if offline access is also enabled. Allow offline enrollment during User Elevation Allow and prompt for offline access enrollment during UAC password elevation if offline access is also enabled. Available in version 4.1.0 and later.
-
Click Next and then Install to complete Duo installation.
If you need to change any of your chosen options after installation, you can do so by updating the registry. See the Duo for Windows Logon FAQ for instructions on how to update the settings.
Test Your Setup
To test your setup, attempt to log in to your newly-configured system as a user enrolled in Duo.

The Duo authentication prompt appears after you successfully submit your Windows credentials. With automatic push enabled (the default installation option), the prompt indicates that Duo pushed an approval request to your phone. Duo sends the push request to the first phone activated for Duo Push and associated with that Duo user.
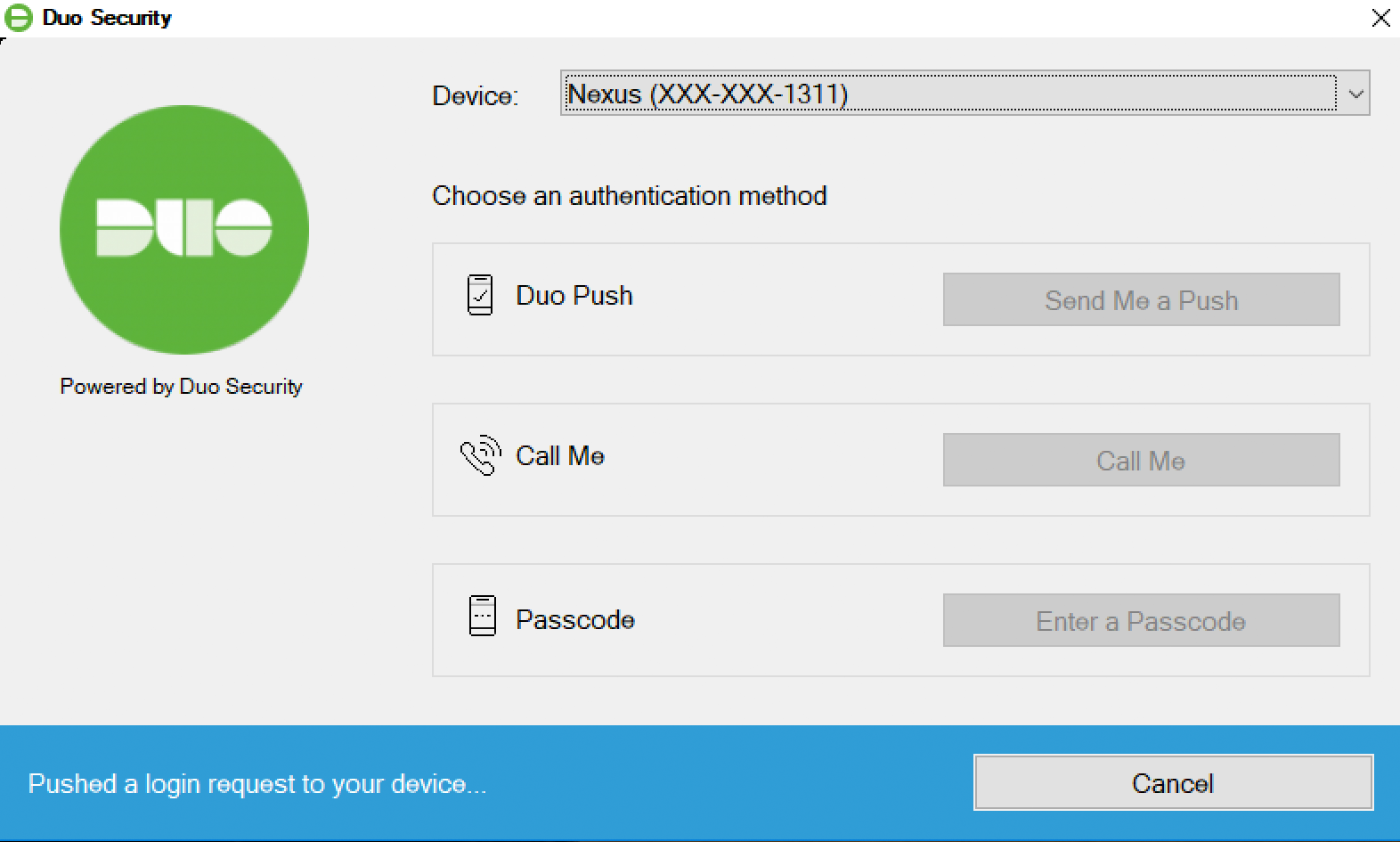
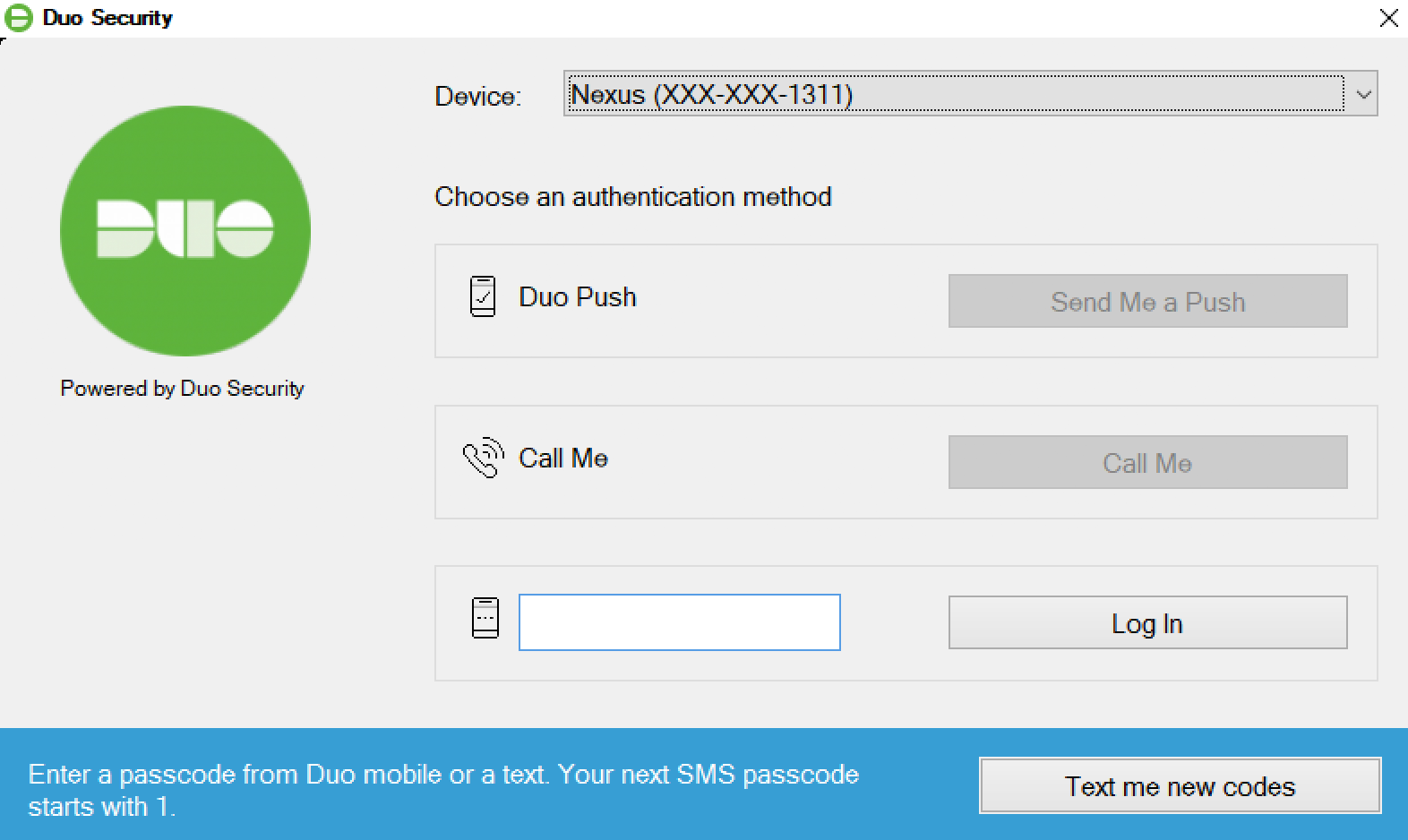
With automatic push disabled, or if you click the Cancel button on the Duo authentication prompt after a 2FA request was sent, you can select a different device from the drop-down at the top (if you've enrolled more than one) or select any available factor to verify your identity to Duo:
- Duo Push: Send a request to your smartphone. You can use Duo Push or Verified Duo Push if you've installed and activated Duo Mobile on your device.
- Call Me: Perform phone callback authentication.
- Passcode: Log in using a passcode generated with Duo Mobile, received via SMS, generated by your hardware token, or provided by an administrator. To have a new batch of SMS passcodes sent to you click the Send me new codes button. You can then authenticate with one of the newly-delivered passcodes.
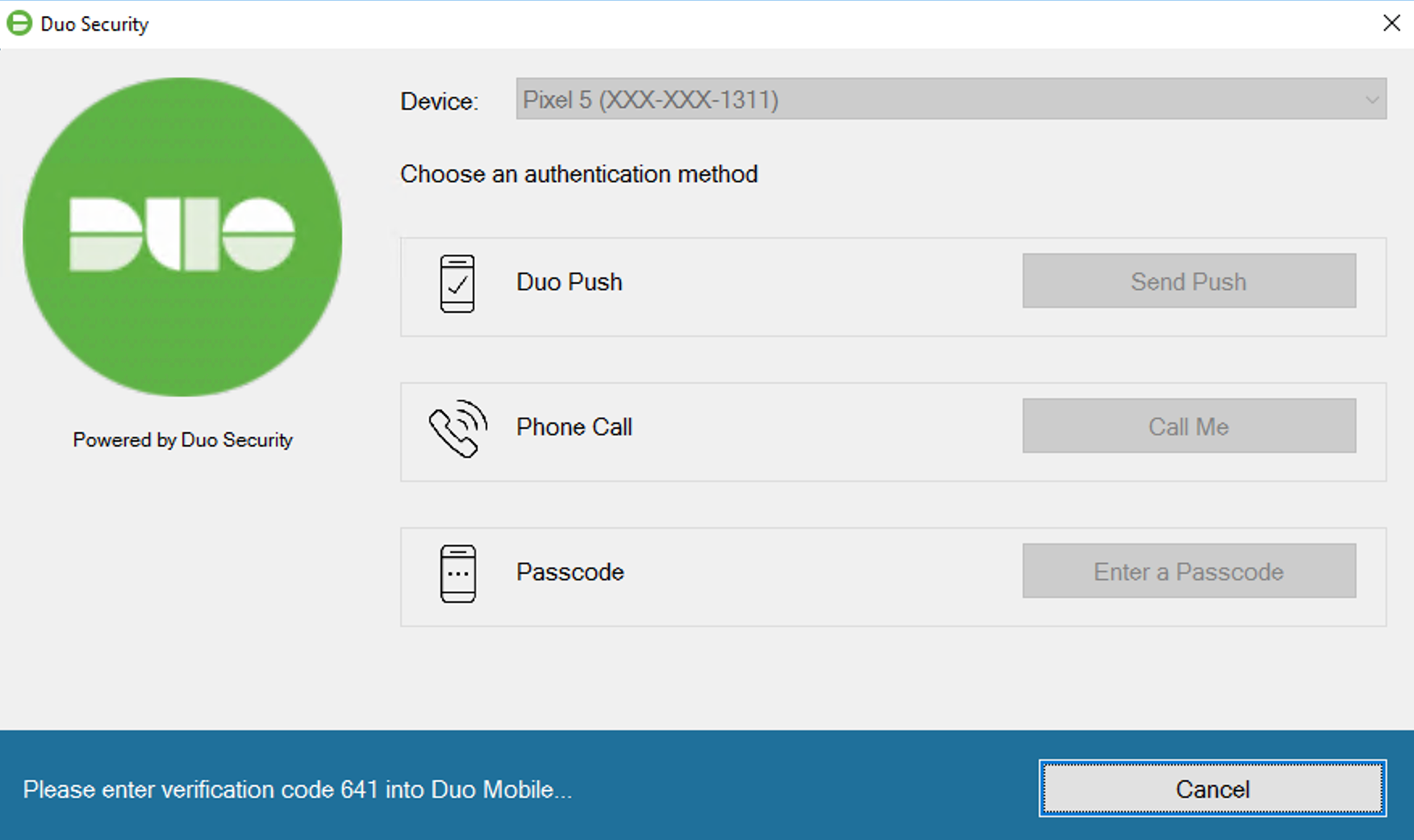
Verified Duo Push
If you applied a policy to your Microsoft RDP application that enables Verified Duo Push with a verification code for Windows Logon, Windows will display a three to six numeric code on-screen when you choose to use Duo Push to log in to that application. Users will need to enter this code into Duo Mobile to approve the login request.
Remembered Device
If you applied a policy to your Microsoft RDP application that enables remembered devices for Windows Logon, then during Duo authentication at the local system's console you'll see the Remember me for... option, reflecting the number of hours or days you set in the policy.
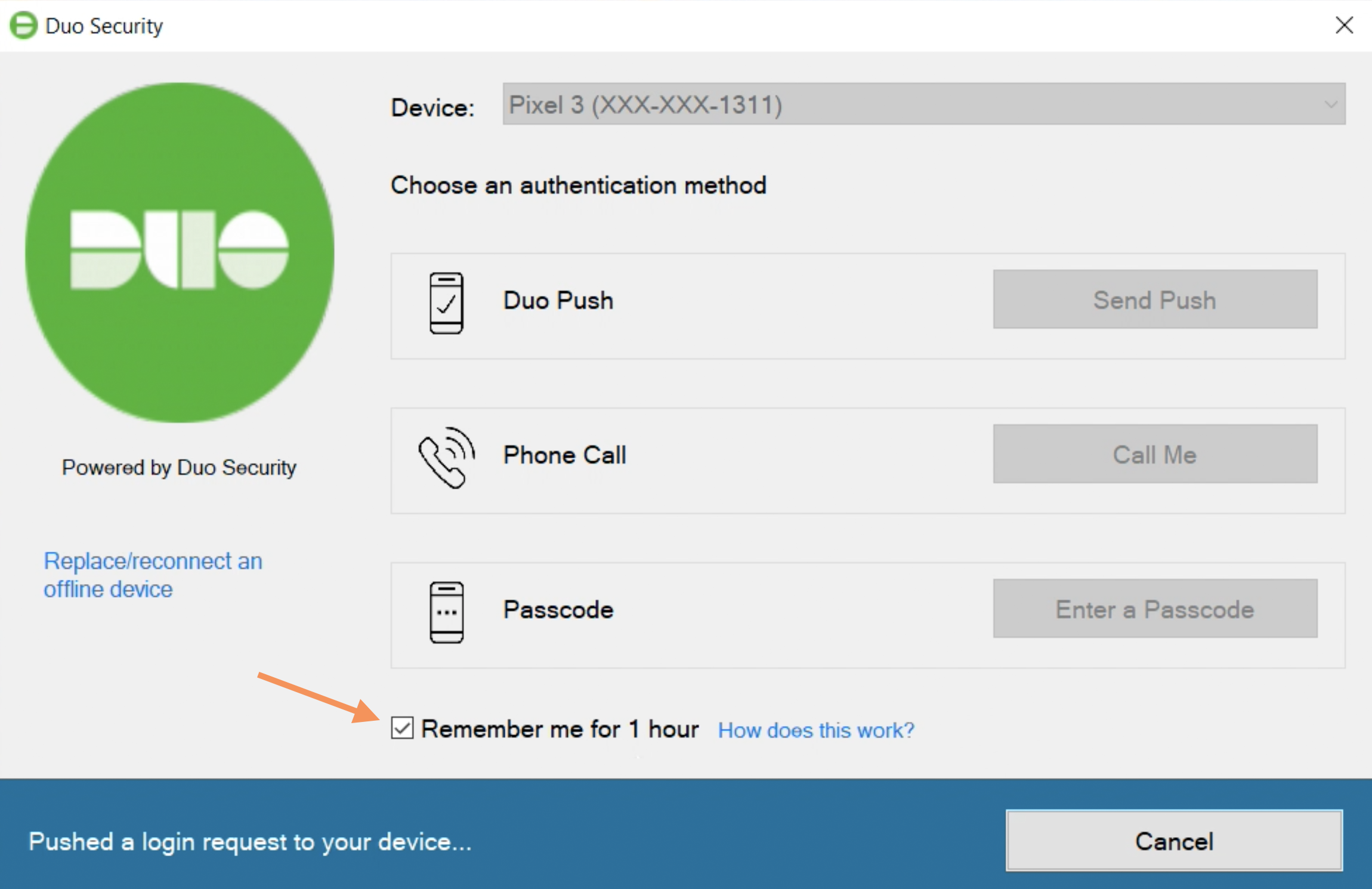
If you check this box when authenticating you won't need to perform Duo second-factor authentication again for the duration specified on the prompt the next time you unlock the workstation to continue the logged-in Windows session.
Duo will prompt you to complete two-factor authentication at the next Windows logon or unlock after the remembered device session ends, and at that time you can choose to begin a new trusted logon session.
UAC Elevation
If you enabled User Elevation in Duo for Windows Logon v4.1.0 or later, you'll see the Duo authentication prompt after you enter your password for a credentialed elevation request. The application you were trying to launch runs after you approve the Duo two-factor request. If you chose to remember the device at the Windows desktop login, then you won't need to approve Duo authentication for UAC elevations made by the same logged-in account either until the trusted Duo session ends.
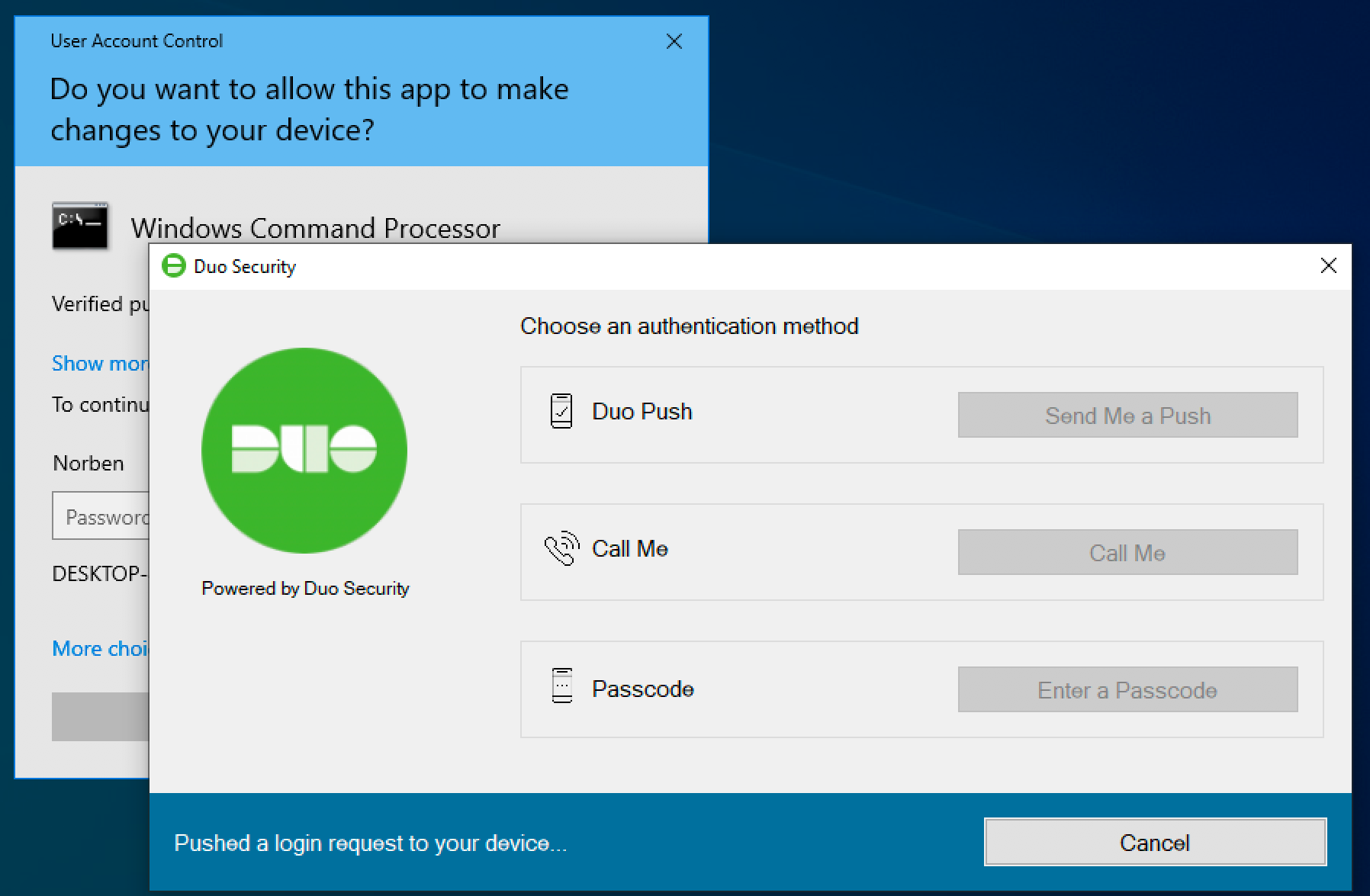
Remember: if you find that Duo Authentication for Windows Logon has locked you out of your Windows system (e.g. due to a configuration error), you can reboot into Safe Mode to bypass it.
See the Duo Knowledge Base article Why are users unexpectedly bypassing 2FA for Windows Logon (RDP)? for additional remediation steps.
Grant Access to Users
If you did not already grant user access to the Duo users you want to use this application be sure to do that before inviting or requiring them to log in with Duo.
Passwordless for Operating System (OS) Logon
Available in: Duo Essentials, Duo Advantage, and Duo Premier
Passwordless for Operating System Logon offers the option to logon without the manual requirement for users to provide a password at OS logon. With Passwordless OS Logon, the password is escrowed to Duo Mobile for secure storage (i.e., there is an arrangement in which the keys (private and public) are needed to decrypt encrypted data). This not only eases users' entry to the OS, it also makes it more difficult for a bad actor to hijack an endpoint machine and then use a stolen password to escalate privileges. Subsequently, Passwordless OS Logon automatically invokes a Bluetooth push for users to authenticate with their biometrics or PIN via Duo Mobile to establish their session.
This is a distinct deployment, enrollment, and authentication experience from Duo Passwordless for Duo SSO web-based applications.
Passwordless for OS Logon Requirements
- Duo Essentials, Advantage, or Premier plan subscription
- Windows 10 21H2 or later or Windows 11.
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM) v2.0 enabled on the Windows device.
- Duo Authentication for Windows Logon 5.0.0 or later installed.
- Bluetooth v4.0 and later enabled on both the Windows and mobile devices.
- Duo Mobile installed and activated for Duo Push.
- Android 12+ and Duo Mobile version 4.64.0 or later.
- iOS 16+ and Duo Mobile version 4.62.0 or later.
- Duo Push enabled as an authentication method in the effective policy for users of the application.
- Windows Hello platform authenticators your users may have registered for Duo Passwordless web-based applications do not work for Windows Passwordless OS Logon.
Note: this solution does not support Remote Desktop connections or virtual machines.
- Supported Bluetooth adapters tested by Duo (only required for computers that don't have Bluetooth built-in):
- Avantree DG45 Bluetooth USB adapter
- Ugreen CM656 Bluetooth adapter
- TP Link UP500
Other Bluetooth adapter models not tested by Duo may work. We strongly suggest you test Passwordless for OS Logon with one of the Bluetooth adapters you plan to use before purchasing them for all your users.
Use a machine that you are able to boot into Safe Mode with Admin access, in case you do get locked out of the Windows system by the Duo client.
Test with Pilot Users
You have two options for testing Passwordless OS Logon with groups of pilot users before expanding it to all users of a given Duo Microsoft RDP application:
-
Create a new Microsoft RDP application in Duo with the Passwordless logon setting enabled for all users in the new application, and then use the integration key and secret key from the new application when you install the 5.0.0 Duo Authentication for Windows Logon release on the Windows systems belonging to your test users.
- After your successful pilot testing update the Duo installations on additional system to use the new Duo Microsoft RDP application, or update the configuration of existing Microsoft RDP applications to also allow Passwordless OS Logon.
-
Identify Duo groups containing your pilot users and then when you enable Passwordless for OS Logon in your existing Microsoft RDP application select those Duo pilot groups in the Limit access by groups option.
- After your successful pilot testing remove the pilot groups from the configuration to apply to all users, or add additional user groups to expand to selected users.
Passwordless for OS Logon Configuration
-
Return to your Microsoft RDP application page in the Duo Admin Panel. You may have given the RDP application a different name when you created it, but the "Application Type" will always be "Microsoft RDP" in your applications list.
-
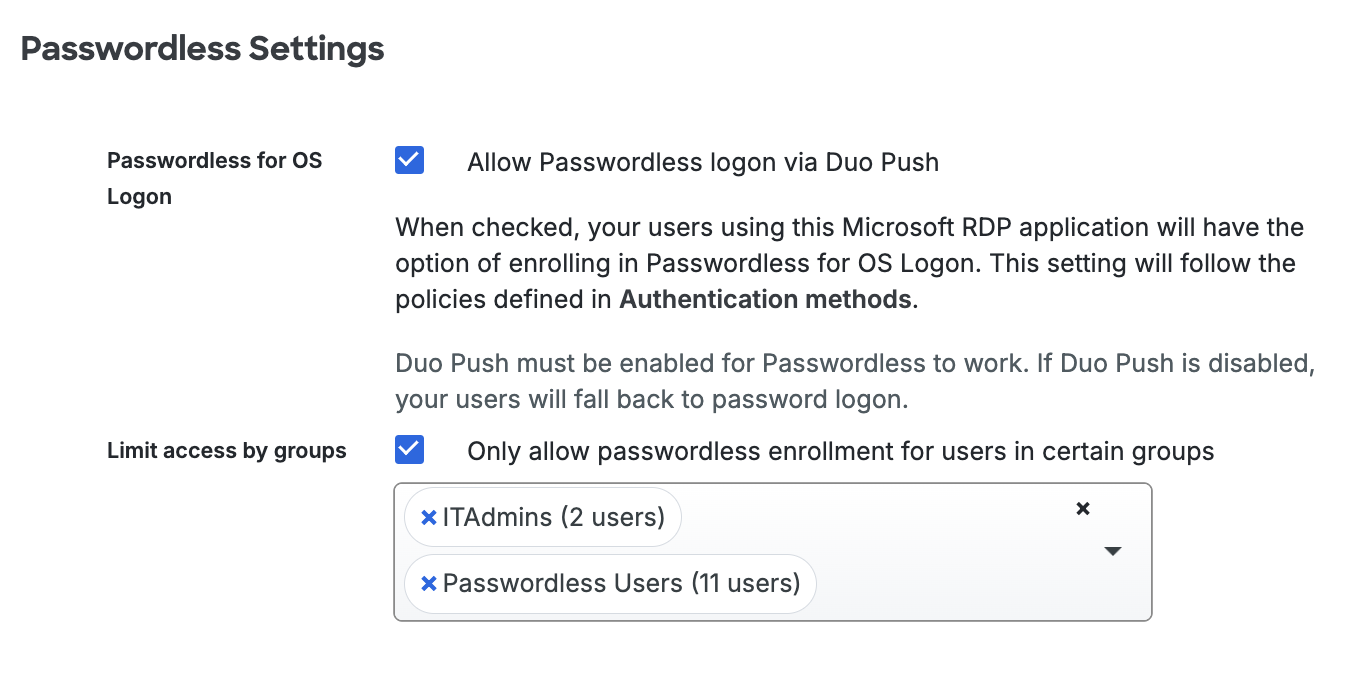
Scroll down to the bottom of the RDP application’s page to locate the Passwordless Settings. Check the box next to Allow Passwordless logon via Duo Push to enable passwordless for OS Logon.
When checked, users of this Microsoft RDP application will have the option of enrolling in Passwordless for OS Logon during local console logins. For this setting to work, Duo Push must also be enabled in your Duo policies as an allowed authentication method. Or if the user doesn't have a device activated for Duo Push, users will fall back to password logon.
-
Check the Limit access by groups option to specify a group or groups of Duo users permitted to enroll in and use Passwordless OS Logon. Users who are not members of the groups you select here will continue using a password to log in to Windows.
-
Click the Save button.
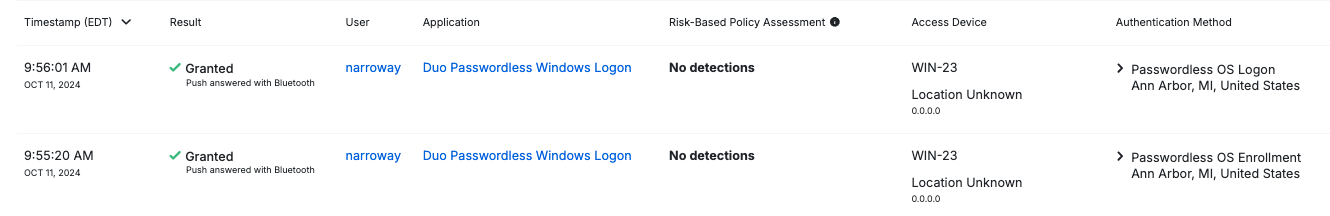
Passwordless Logging
You will be able to see users that have access granted or denied, as well as Passwordless OS enrollment and Passwordless OS Logon as newly listed authentication methods in the Authentication logs.
Passwordless OS Logon Enrollment and Login
The next time a user logs in to or unlocks the workstation while it’s online and able to contact Duo, the passwordless enrollment prompt displays after successful two-factor authentication.
Step through the guided enrollment process to setup passwordless authentication on that Windows system.
Once you’ve enrolled in Passwordless OS Logon, you will no longer need to enter a password to logon to that Windows system. If you log in to multiple Windows systems you'll need to repeat the setup steps on each one to log in without a password.
Duo Mobile cannot restore Passwordless OS Logon accounts on a new mobile device. If you log on with a different mobile device, you'll need to repeat the setup steps to log on to the same or different Windows system without a password.
See the full Passwordless OS Logon enrollment and authentication experience in the Duo User Guide for Windows Logon.
If users have issues with Passwordless OS Logon setup or use please see Duo Knowledge Base article 9088 for troubleshooting guidance.
Offline Access
Duo Authentication for Windows Logon v4.0.0 introduces offline access, allowing secure local logons to Windows systems even when unable to contact Duo’s cloud service.
Offline Access Requirements
- Duo Essentials, Advantage, or Premier plan subscription
- Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 4.0.0 or later
- Disable the Bypass Duo authentication when offline (FailOpen) option. If you enabled FailOpen during installation, you can change it in the registry.
- Disable the Only prompt for Duo authentication when logging in via RDP option to use offline access with laptop or desktop local console logins. If you enabled Duo for RDP logins only during installation, you can change it in the registry.
Users must have either:
- Duo Mobile for Android or iOS version 3.22 or later (no Windows Phone support)
- One of the following supported U2F security key - ensure the key you plan to use does not require extended length encoding:
We strongly suggest you test offline access with one of the security keys you plan to use before purchasing them for all your users.
HyperFIDO tokens are not supported for offline access activation, nor are simple OTP passcode tokens or Duo D-100 hardware tokens.
Note these functional limitations for offline access authentication devices:
- Users may only register one authenticator for offline access, so it is not possible to register backup devices for approving offline login. Registering a second offline device deactivates the first one.
- U2F security keys for offline authentication only work for local system console logins. It is not possible to use a security key attached to your local RDP client system to perform offline authentication at a remote Windows server. You can use a Duo Mobile offline passcode with a remote system.
- Remembered devices policy settings and local trusted sessions do not apply to offline access. If you choose to remember the device when you log in while online, and then unlock the Windows workstation while offline, the previously created trusted session ends and you will need to complete offline access authentication. When the workstation is back online, you will need to complete online Duo authentication to begin a new remembered device session.
Offline Access Configuration
-
Return to your "Microsoft RDP" application page in the Duo Admin Panel. You may have given the RDP application a different name when you created it, but the "Application Type" will always be shown as "Microsoft RDP" on the Applications page.
-
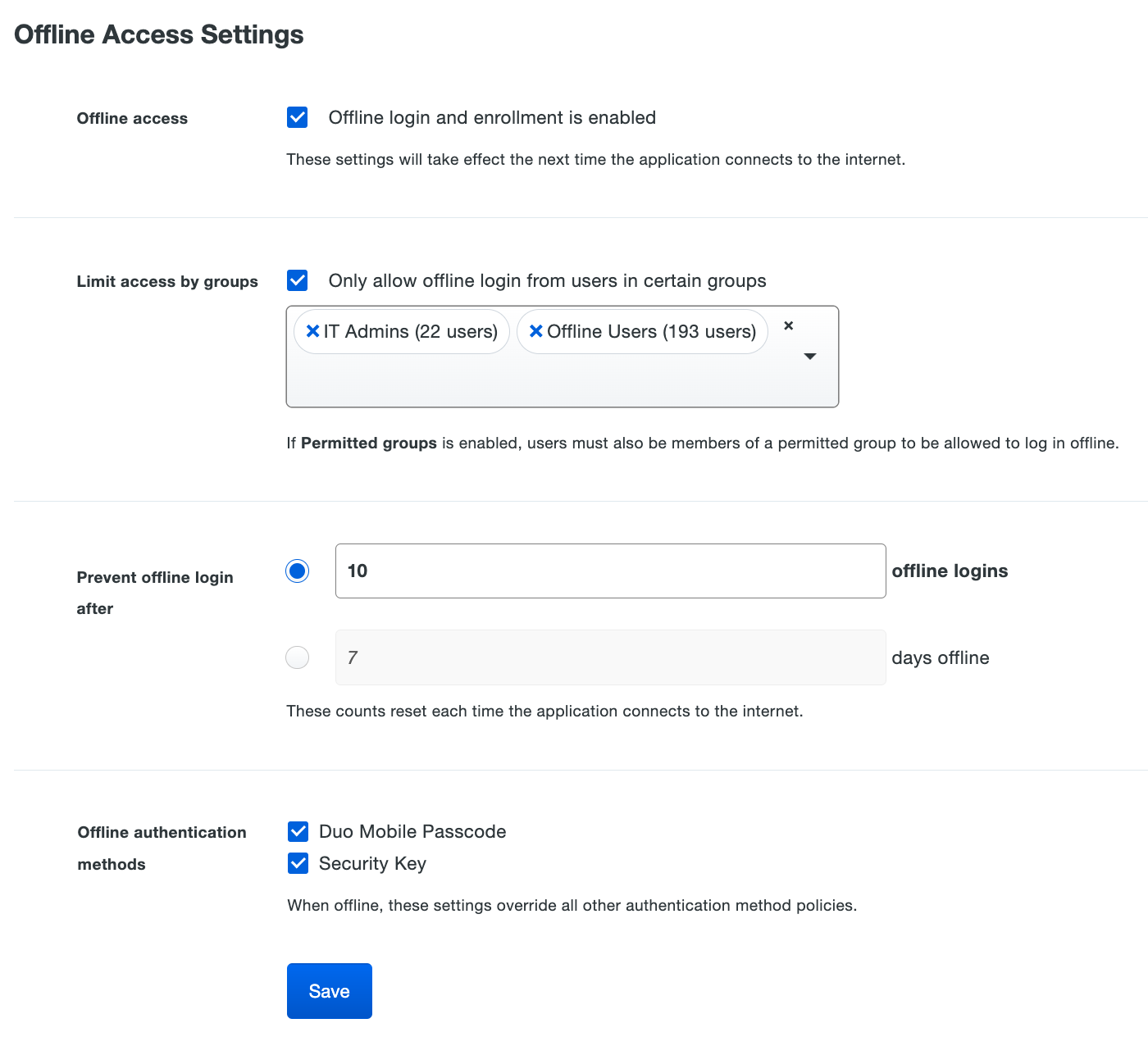
Scroll down to the bottom of the RDP application’s page to locate the Offline Access Settings. Check the box next to Enable offline login and enrollment to turn on offline access.
-
Check the Only allow offline login from users in certain groups to specify a group or groups of Duo users permitted to use offline access. Users who are not members of the groups you select here won't be able to enroll in offline access or login in with MFA when the Windows system is unable to contact Duo, and instead are subject to your fail mode configuration (let in without MFA if you enabled fail open, or prevented from logging in if you disabled fail open).
After you configure this option, when a user logs into a Windows system while it's online and can reach Duo and it has been greater than 24-30 hours since the last online authentication, Duo for Windows Logon will update the offline policies for all users on the system, including deprovisioning them for offline access if they are no longer members of the offline groups selected for offline login in the Duo Admin Panel.
If you also restricted user access to select permitted groups on your RDP application, users need to be members of both the permitted and the offline login groups to use offline access.
-
Choose from the two options for expiring offline access in the Prevent offline login after setting:
-
Enter the maximum number of offline logins allowed to users. With this option, there is no expiration date for offline access.
Users may log on to the Duo-protected Windows workstation while offline the number of times you specify here. They'll need to reconnect their offline computer to the internet upon reaching this limit. The next time they perform an online Duo authentication, the computer’s offline counter resets.
-
Enter the maximum number of days offline, up to 365. With this option, there is no limit to the number of times a user logs in while offline during the allowed period.
Users need to reconnect their offline computer to the internet upon reaching the end of the period you define here. The next time they perform an online Duo authentication, the computer’s offline expiration date resets. If the user does not perform online Duo authentication before the maximum number of days specified here is reached, they can no longer log in offline, and so must connect to Duo's service in order to log in at all.
-
-
Users may activate offline access using either the Duo Mobile application for iOS or Android, or a U2F security key. Both offline authentication methods are allowed unless you uncheck one in the Offline authentication methods setting. You may not uncheck both options.
Any authentication method enabled for offline access is always permitted, overriding any other policy setting restricting authentication methods for the RDP application.
-
Click the Save button.
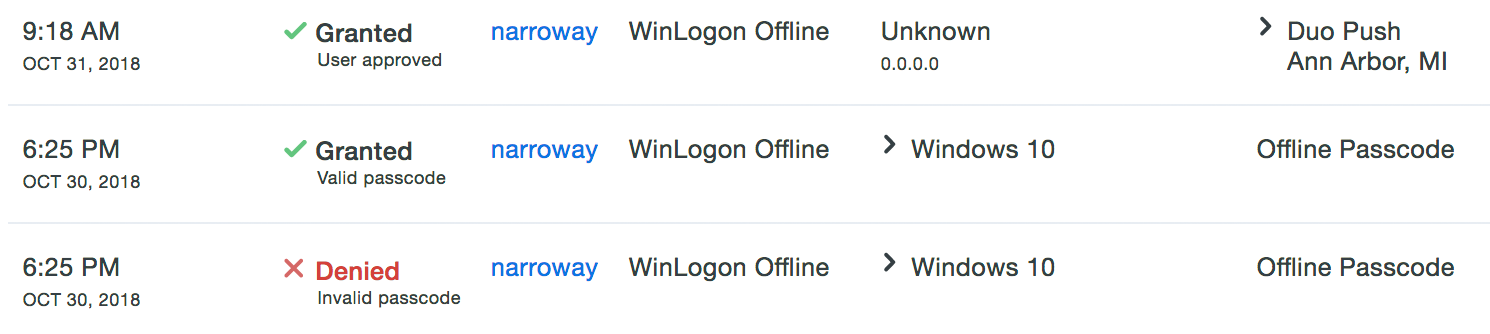
Offline Access Logging
No information about logins using offline access is reported in Duo Admin Panel authentication reports while the Windows system is offline. At the next online authentication, login events that occurred while the system was offline are sent to Duo's service. These events show up in the Authentication Log with other user access results, and show the offline authentication method used.
Advanced Configuration
Change How Many Users May Use Offline Access
By default, five (5) users may enroll in offline access. To increase or reduce the number of users that may activate offline access on a given Windows client, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
OfflineMaxUsers
|
|
Create this value and set to the number of users you would like to have the ability to enroll in offline access on a given Windows system. Minimum value: 1; Maximum value: 50. If not set the default is 5.
|
|
Once the maximum number of users have activated offline access, the next user receives an error when attempting to enroll in offline access.
Force Offline Reactivation for a User
To force offline reactivation for a previously activated user on a given Windows system, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to delete the entire registry key that includes the username from HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv\Offline.
Prevent Offline Access Use on a Client
You may have Windows systems where no users should log in using offline access, regardless of the application setting in the Duo Admin Panel. To prevent offline authentication for any user on a given Windows client, use the Registry Editor (regedit.exe) with administrator privileges to create or update the following registry value:
Location: HKLM\SOFTWARE\Duo Security\DuoCredProv:
| Registry Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
OfflineAvailable
|
|
Create this value and set to 0 to disable offline access for all users. Your fail mode configuration applies to offline logins (either fail open or fail closed).
|
|
Offline Access Activation and Login
The next time you (or your end user) logs in to or unlocks the workstation while it’s online and able to contact Duo, the offline activation prompt displays after successful two-factor authentication.
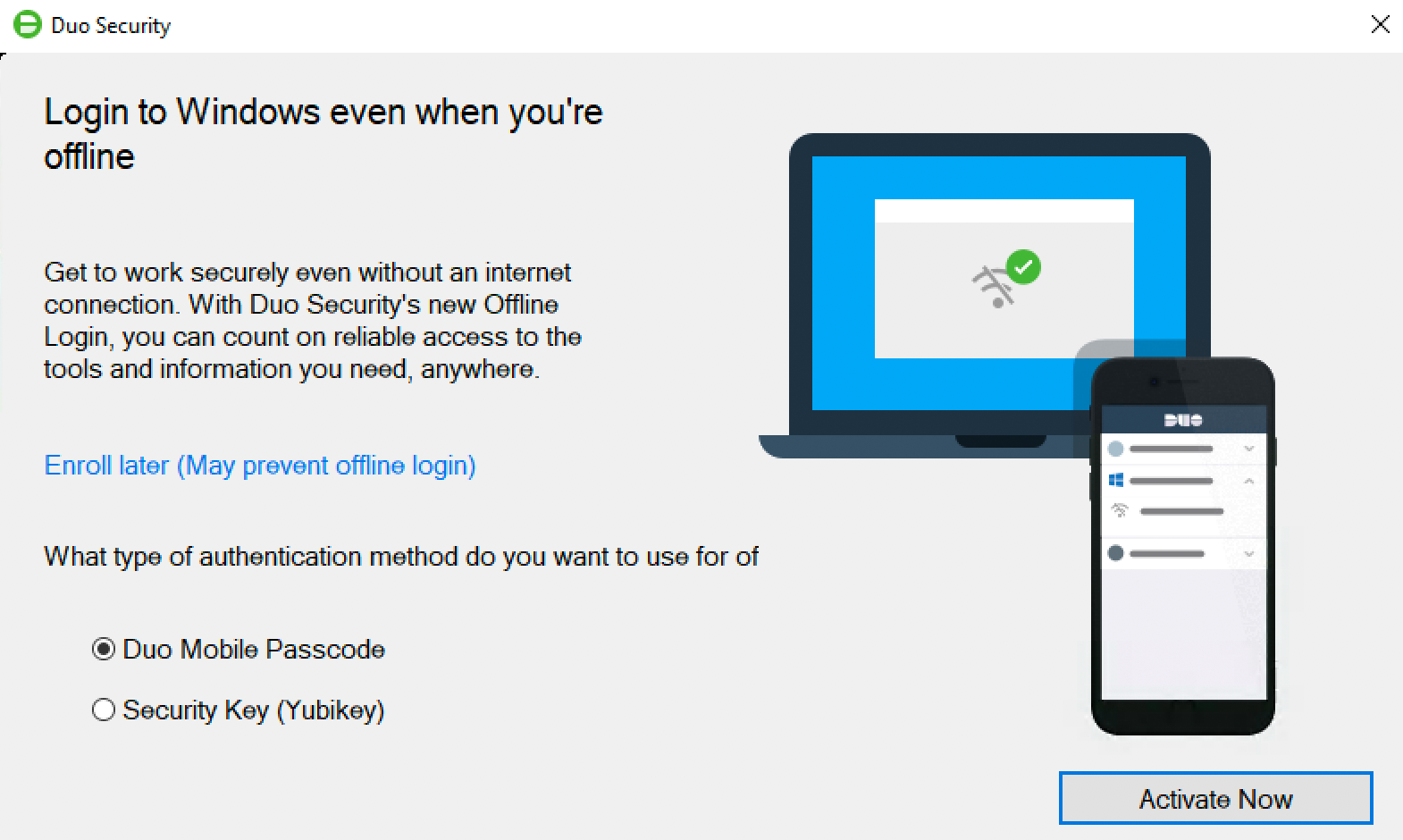
Step through the guided activation process to configure Duo Mobile or a U2F security key for offline MFA.
Once you’ve activated offline access for your account, when your computer isn’t able to contact Duo’s cloud service you’ll automatically be offered the option to login with an offline code or security key after successfully submitting your Windows username and password.
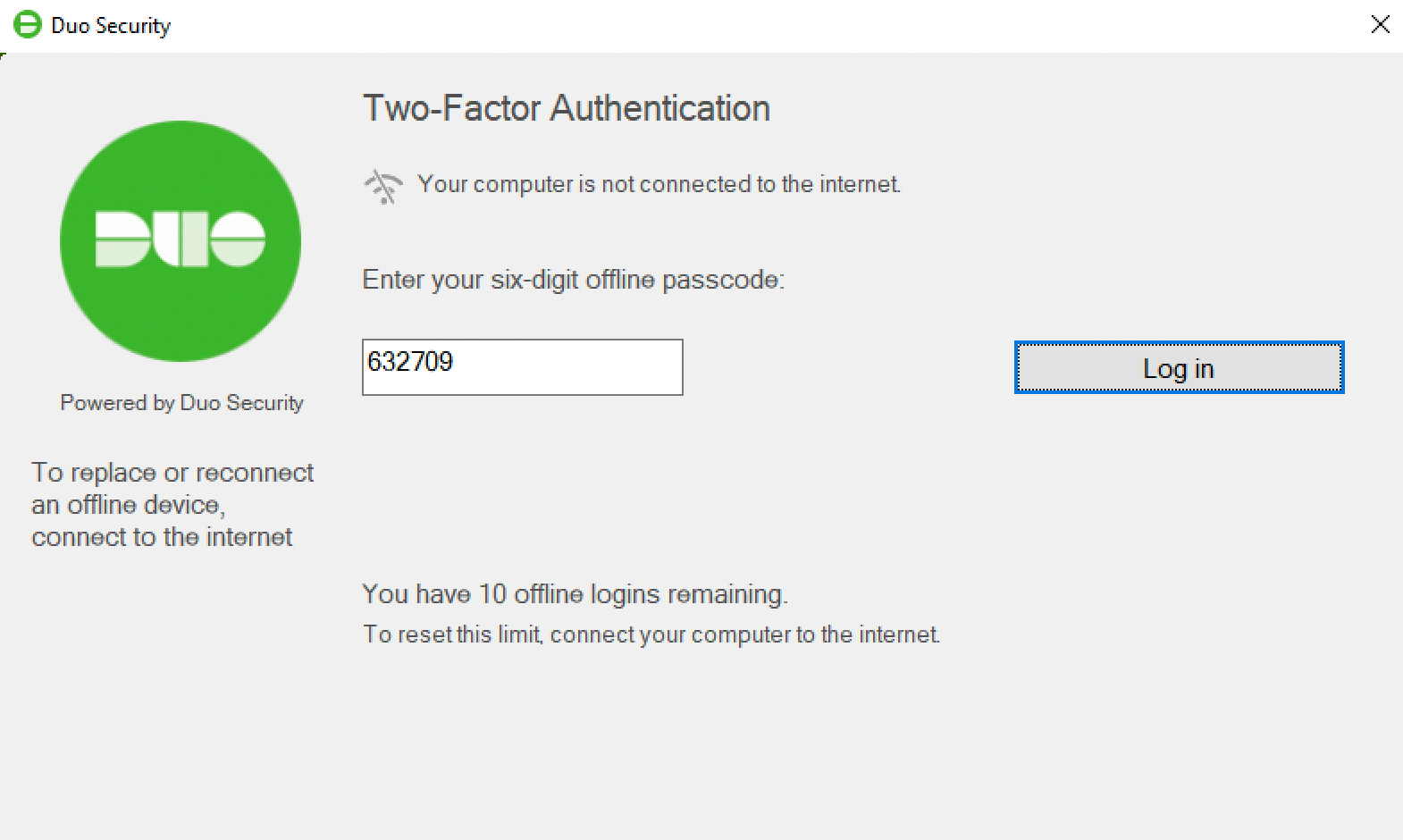
You can also reactivate offline access from the online Duo prompt. Note that only one authentication device — a single phone with Duo Mobile or a single security key — may be activated for offline login. Activating a second device via the reactivation process deactivates the first.
See the full offline activation and login experience in the Duo User Guide for Windows Logon.
Updating Duo Authentication for Windows Logon
Modifications made to the Duo Authentication for Windows Logon version 4.3.1 installer result in direct upgrades from version 4.3.0 to version 4.3.1 leaving the program information for 4.3.0 visible in Add/Remove Programs and the registry. This does not affect the installed 4.3.1 application's operation. See the Duo for Windows Logon FAQ for more information.
You can upgrade your Duo installation over the existing version; there's no need to uninstall first. The installer maintains your existing application information and configuration options.
-
Download the most recent Duo Authentication for Windows Logon installer package. View checksums for Duo downloads here.
-
Run the installer with administrator privileges and follow the on-screen prompts to complete the upgrade installation.
If you're upgrading to a version that includes new installer options, the configuration screen for those options won't be shown during an upgrade install. You'll need to configure those new options via Regedit or GPO update. See the Configuration section of the FAQ to learn how to enable and configure Duo for Windows Logon options in the registry, or the Group Policy documentation to learn how to configure options with GPO.
Uninstalling Duo
If you'd like to remove Duo Authentication for Windows Logon from your system, open the Windows Control Panel "Programs and Features" applet, click on the "Duo Authentication for Windows Logon" program in the list, and then click Uninstall.
Do not delete the Microsoft RDP application from the Duo Admin Panel until you have uninstalled the Duo application from all Windows systems using that application. If you delete the Admin Panel application before uninstalling the Duo software you may block users from logging in to Windows.
Advanced Deployment and Configuration using Group Policy
Please see our Duo Authentication for Windows Logon Group Policy documentation.
Troubleshooting
Need some help? Take a look at the Windows Logon Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) page or try searching our Windows Logon Knowledge Base articles or Community discussions. For further assistance, contact Support.
If the Duo application denies access to your users, ensure that you have enrolled them in Duo with a username or username alias that matches the username they use to log into Windows, and with a 2FA device attached that is activated for Duo Push, can receive phone calls from Duo, or can generate a one-time passcode. If you applied a new user policy that allows access without 2FA expecting it to allow the blocked users through, this only has effect if the blocked users do not exist in Duo. Refer to these articles to learn more about user enrollment states and how they combine with policy settings to affect user logins.
- Why are Duo users being prompted to enroll or denied access when my New User Policy is set to allow access without 2FA?
- Guide to Duo User Enrollment States
Network Diagram
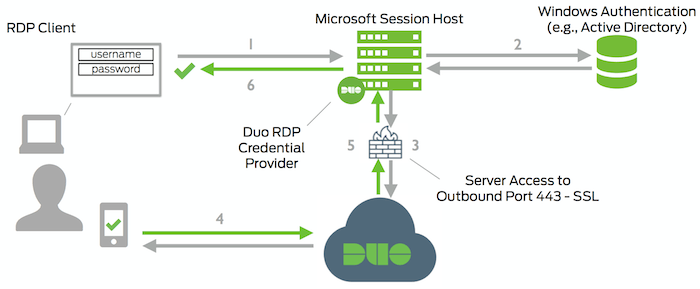
- RDP connection, console logon, or UAC elevation initiated
- Primary authentication of Windows credentials (domain or local user)
- Duo Windows Logon credential provider connection established to Duo Security over TCP port 443
- Secondary authentication via Duo Security’s service
- Duo Windows Logon credential provider receives authentication response
- RDP or console session logged in
Video Overview
Videos show the Duo Admin Panel experience prior to November 2024, Duo for Windows Logon installations prior to version 4.3.0, and Duo Mobile version 3.
