Duo Single Sign-On for Generic OpenID Connect (OIDC) Relying Parties
Last updated:
About Duo Single Sign-On
Duo Single Sign-On is our cloud-hosted SSO product which layers Duo's strong authentication and flexible policy engine on top of your relying party application logins using the Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) 2.0 or OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication standards. Duo Single Sign-On acts as an OpenID provider (OP), authenticating your users using existing on-premises Active Directory (AD) or any SAML 2.0 IdP and prompting for two-factor authentication before permitting access to your relying party application.
Duo Single Sign-On is available in Duo Premier, Duo Advantage, and Duo Essentials plans, which also include the ability to define policies that enforce unique controls for each individual SSO application. For example, you can require that Salesforce users complete two-factor authentication at every login, but only once every seven days when accessing your relying party application. Duo checks the user, device, and network against an application's policy before allowing access to the application.
Configure Single Sign-On
Before configuring your relying party application with Duo SSO using OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication you'll first need to configure a working authentication source.
Once you have your SSO authentication source working, continue to the next step of creating the your relying party application application in Duo.
When configuring an application to be protected with Duo Single Sign-On you'll need to send attributes from Duo Single Sign-On to the application. Active Directory will work with no additional setup, but if you used a SAML identity provider as your authentication source please verify that you configured it to send the correct SAML attributes.
These default attributes automatically map certain attributes from your authentication source.
| Default Attribute | Active Directory | SAML IdP |
|---|---|---|
<Username> |
sAMAccountName | Username |
<Email Address> |
||
<Display Name> |
displayName | DisplayName |
<First Name> |
givenName | FirstName |
<Last Name> |
sn | LastName |
<AMR> |
Not Applicable | Not Applicable |
AMR will be reported as [`pwd`, `auth-factor-dependent`].
Create Your Cloud Application in Duo
-
Log in to the Duo Admin Panel and navigate to Applications → Application Catalog.
-
Locate the entry for Generic OIDC Relying Party with the "SSO" label in the catalog. Click the + Add button to start configuring Generic OIDC Relying Party. See Protecting Applications for more information about protecting applications with Duo and additional application options. You'll need the information on the Generic OIDC Relying Party page under Metadata later.
-
No active Duo users can log in to new applications until you grant access. Update the User access setting to grant access to this application to users in selected Duo groups, or to all users. Learn more about user access to applications. If you do not change this setting now, be sure to update it so that your test user has access before you test your setup.
This setting only applies to users who exist in Duo with "Active" status. This does not affect application access for existing users with "Bypass" status, existing users for whom the effective Authentication Policy for the application specifies "Bypass 2FA" or "Skip MFA", or users who do not exist in Duo when the effective New User Policy for the application allows access to users unknown to Duo without MFA. -
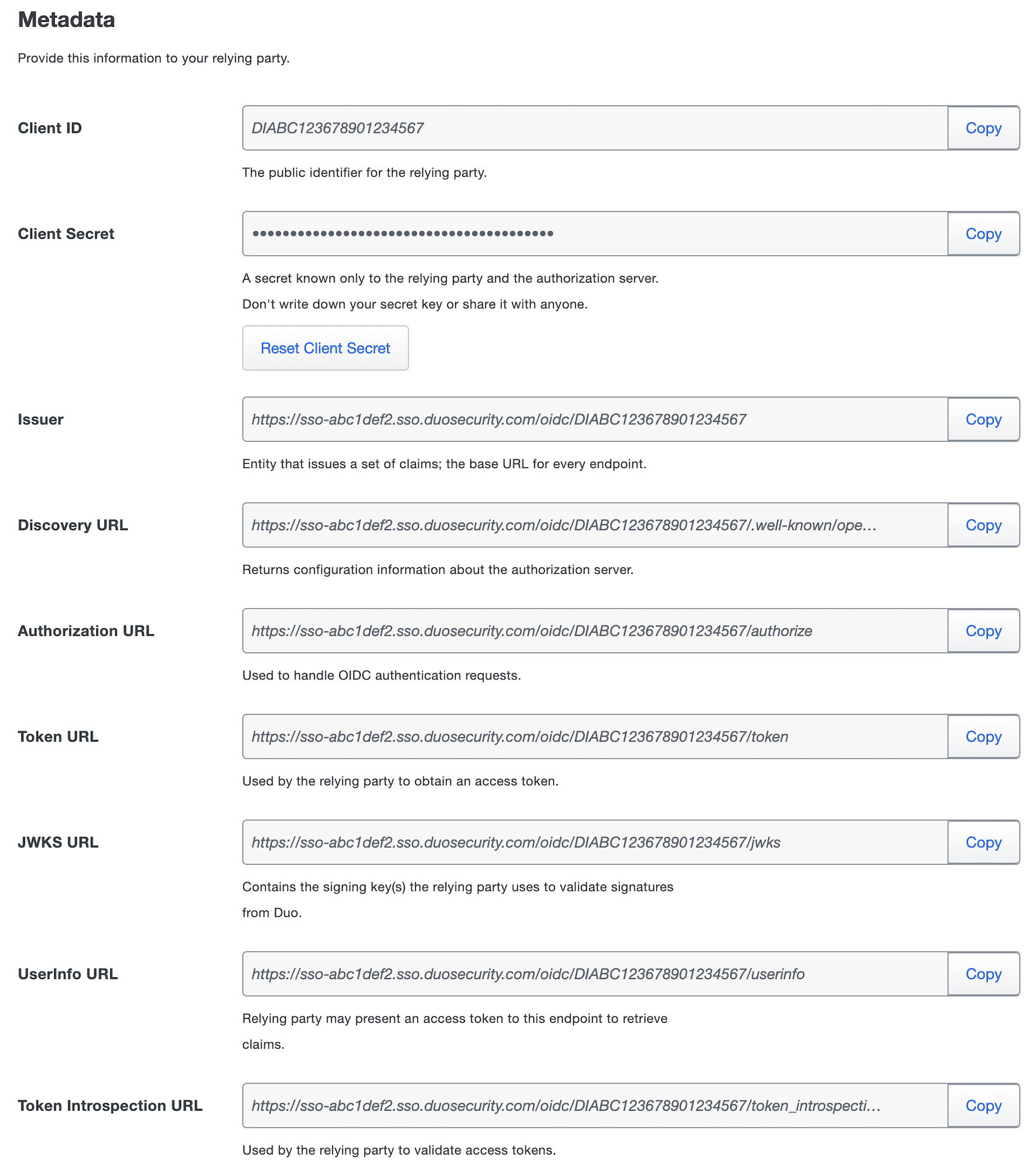
The Metadata section is where you can get OpenID provider information about Duo Single Sign-On to provide to your relying provider.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Client ID | The public identifier of the relying party. |
| Client Secret | A secret that is only held by the relying party and OpenID provider. This secret is used to make authenticated requests against the OpenID provider. You can reset the secret by clicking the Reset Client Secret button. Once the secret is reset the old secret will be rejected. |
| Issuer | Unique entity related to the OpenID provider that issues a set of claims. This is also the base URL of every endpoint below. |
| Discovery URL | Returns basic information about OpenID provider such as endpoint URLs and supported configuration methods. This will also include the supported scopes for this OpenID provider once this page has been configured and saved. |
| Authorization URL | URL that the relying party will redirect the user's browser to along with an authentication request. |
| Token URL | URL used by the relying party to retrieve the access, id, and refresh tokens after a user has successfully authenticated to the OpenID provider. |
| JWKS URL | URL that returns a list of signing keys to validate the signatures of JWTs signed by this OpenID provider. |
| UserInfo URL | URL where relying party can present access token to retrieve information about the token. |
| Token Introspection URL | URL where relying party can validate an access token. |
Configure Your Relying Party
You'll need to provide some information about Duo Single Sign-On to your cloud application provider, like URL information, client ID, and client secret. You can find this information in the Metadata section at the top of the application page in the Duo Admin Panel.
Refer to your relying party's SSO configuration guide for instructions.
Update your Application in Duo
-
Return to the application page in your Duo Admin panel.
-
Navigate to the Relying Party section and provide information from your relying party:
Name Description Grant Type Modify the authorization code and/or refresh tokens. Name Description Authorization Code Under "Authorization Code" you can configure a few additional settings:
- Allow PKCE only authentication: Checking this box will allow Single Page Applications (SPAs) that are unable to store a client secret to retrieve tokens by just completing a Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) authentication.
- Access Token Lifetime: This is the length of time an issued access token is valid for. The lifetime can be 5 to 60 minutes. Default is 60 minutes.
Refresh Tokens Refresh tokens enable the relying party to request and be issued a refresh token, which can then be used to obtain updated access, id, and refresh tokens without requiring the user to log in interactively again. A refresh token will be issued if the authentication request includes
offline_accessas one of the requested scopes.
After checking the box next to "Refresh Tokens", you can configure a few additional settings:
- Refresh Token Absolute Lifetime: The length of time after an original user authentication that refresh tokens can be exchanged for additional tokens. Once this time has been exceeded, the user will need to authenticate again. The lifetime can be 60 minutes to 180 days. Default is 30 days.
- Refresh Token Inactivity Lifetime: The length of time an individual unused refresh token will be valid before it expires. The lifetime can be 5 minutes to 7 days. Default is 24 hours.
Sign-In Redirect URLs The URLs where Duo SSO will send the authentication response based on the redirect URL in the request. Enter the redirect URLs provided by your relying party. Wildcard URLs while not recommended, can be used but must start with "https://" and must only be wildcarding a subdomain.
If you need more than one redirect URL you can enter more by clicking Add Redirect URL.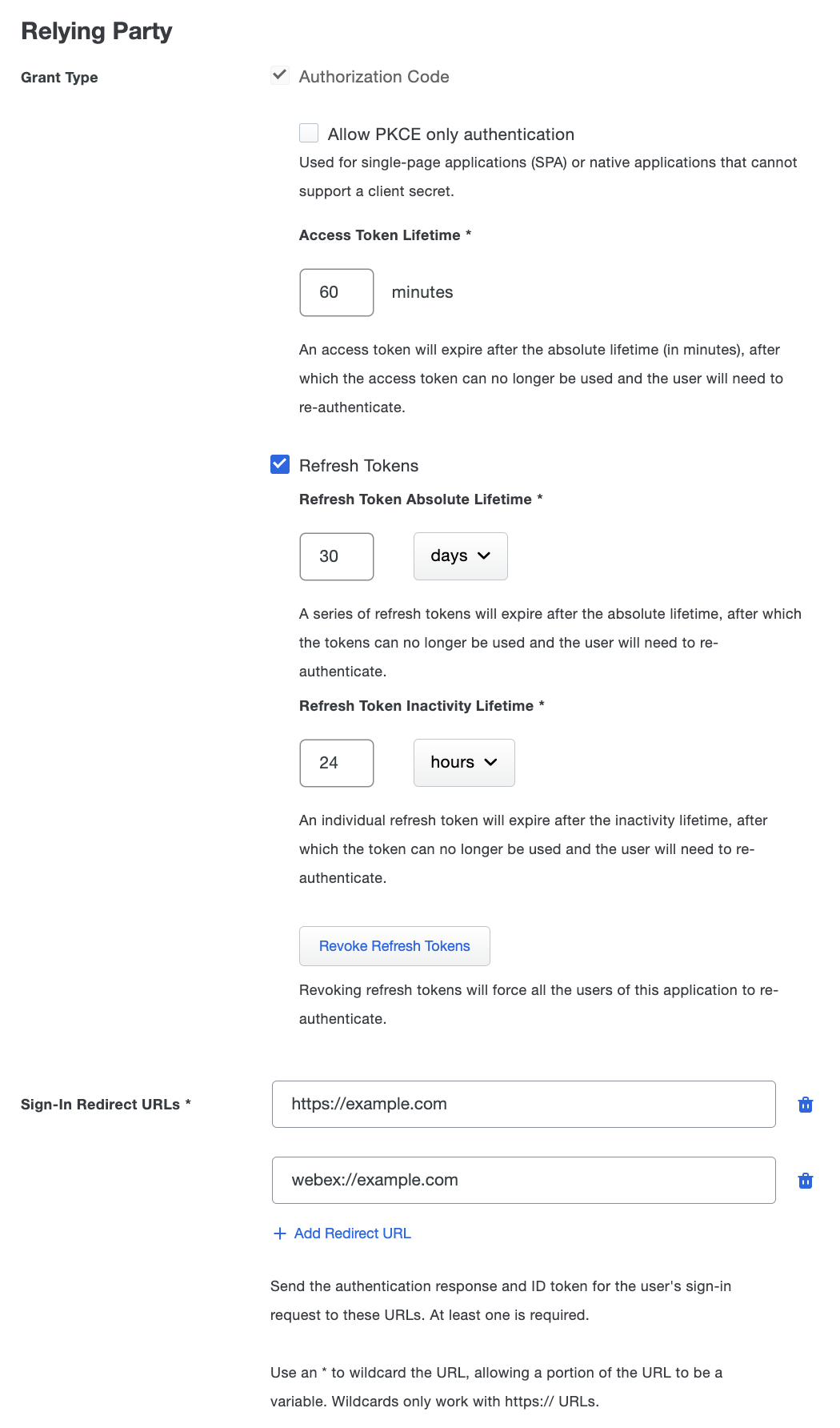
Scopes are used by the relying party during authentication to authorize access to a user's details. Each scope returns a set of user attributes (claims) that are required to be mapped to an IdP attribute. When an OIDC request is sent to Duo SSO only the claims from the requested scopes will be sent back in the response.
Refer to your relying party documentation to complete the OIDC Response section:
Under the Scopes section you'll find checkboxes that show standard scopes that are commonly used in OIDC flows. Once you check a box related to a scope it will expand and show default claims that are already mapped to an authentication source using default attributes. The authentication method reference ('amr') claim is always reported as part of the ID Token. On the left side under IdP Attribute you can select our pre-configured attributes which will automatically pick the correct attribute based on your authentication source from the drop-down or type in the name of an attribute from your authentication source. The right side Claim corresponds to the name of the claim that attribute will be associated with.
Name Description openid A required claimless scope when doing an OIDC authentication. This scope cannot be disabled. profile Checking this box will automatically populate three standard claims given_name,family_name,namemapped to three default attributes. You can change these values or remove them by clicking the trash can icon on the left-hand side. You can add additional claim mappings by clicking Add claim. If enabled, this scope must always have at least one claim.email Checking this box will automatically populate one standard claim emailmapped to a default attribute. You can change these values or remove them by clicking the trash can icon on the left-hand side. You can add additional claim mappings by clicking Add claim. If enabled, this scope must always have at least one claim.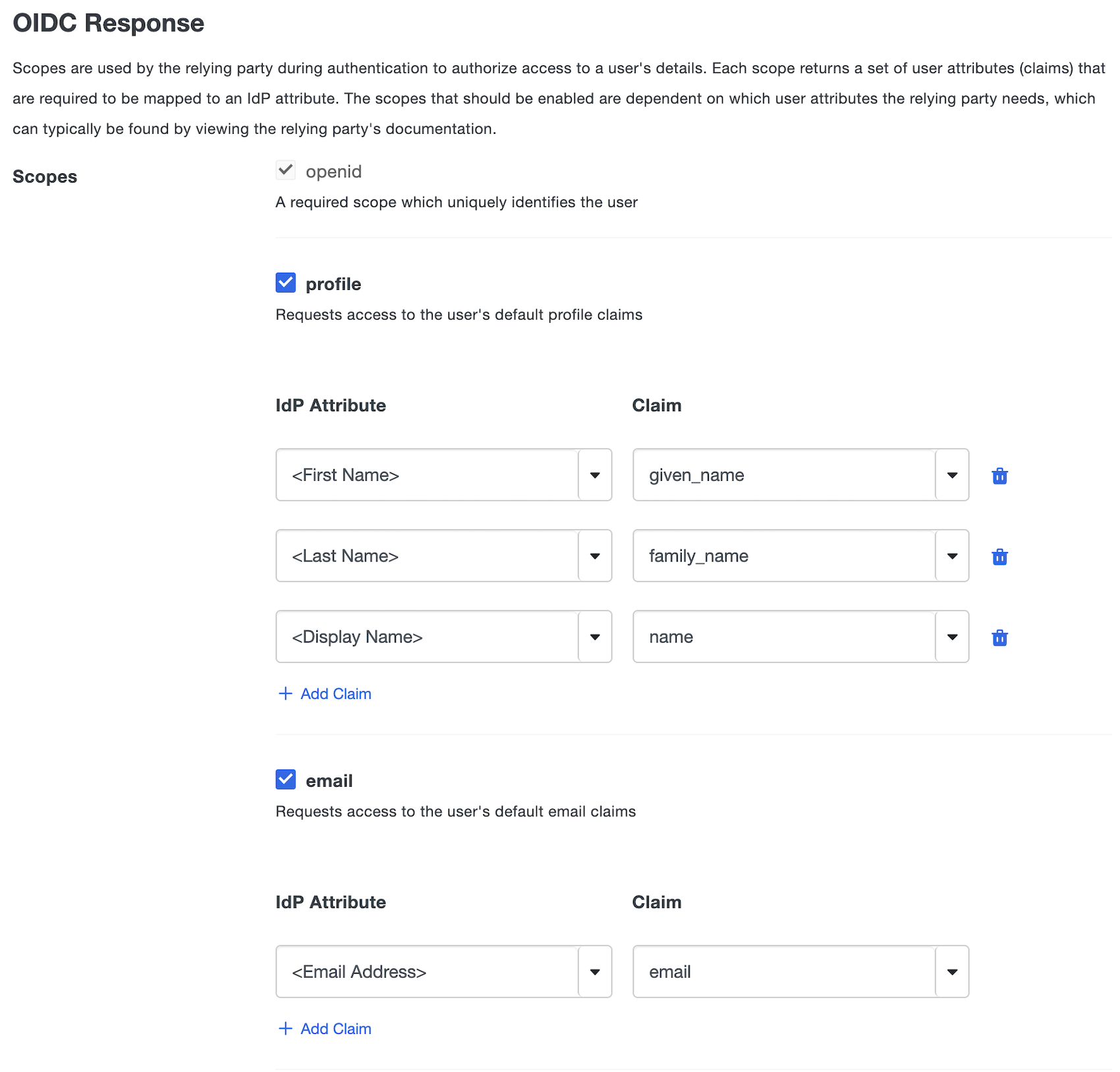
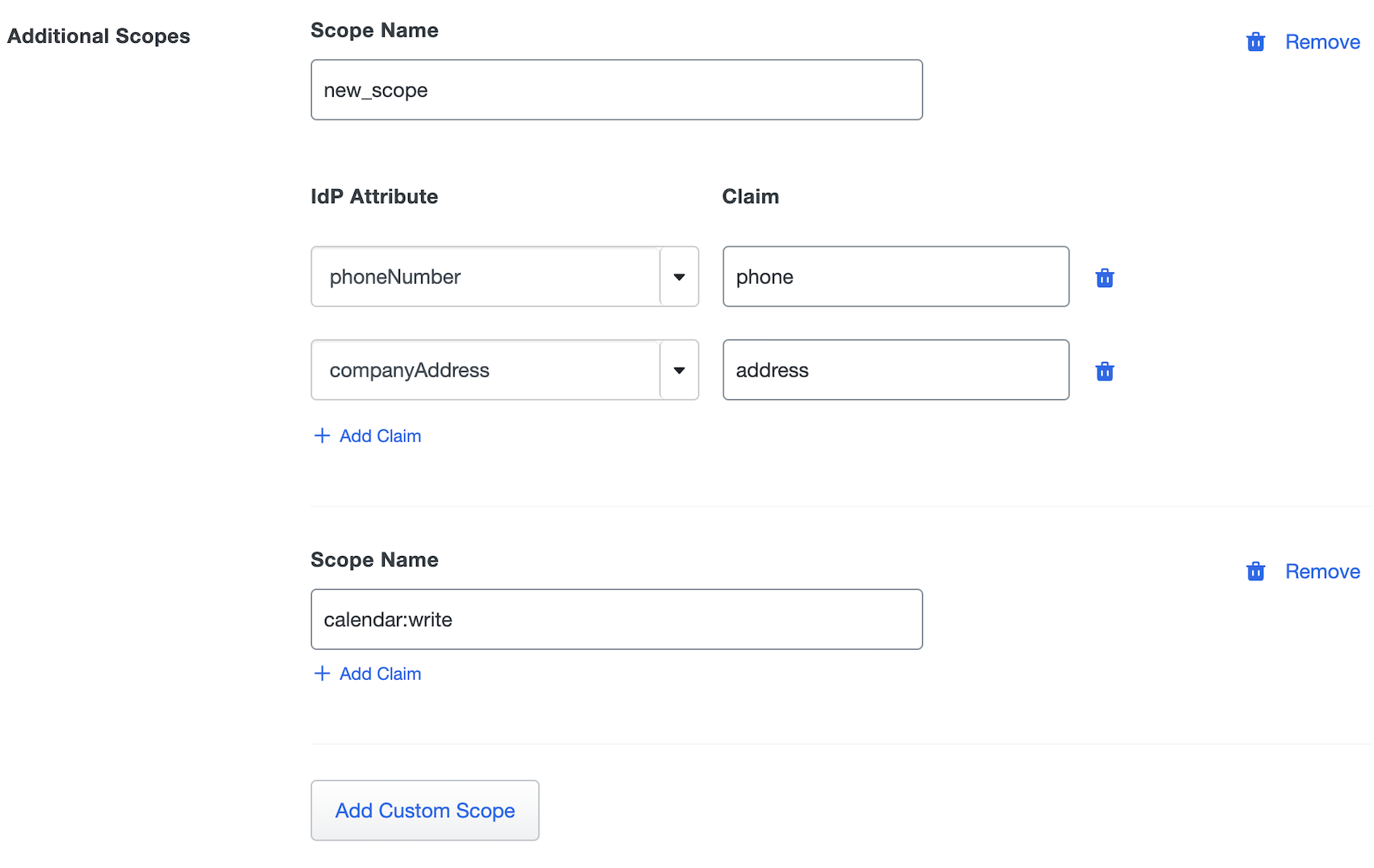
If you require additional scopes you can click the Add Custom Scope button which will allow you to type the name of a scope. If this scope should not contain claims you can continue on or you can click Add Claim under the scope name to add claim mappings for the scope.
You can adjust additional settings for your new SSO application at this time — like changing the application's name from the default value, enabling self-service, or assigning a group policy.
Scroll down to the bottom of the page and click Save.
Claim Transformations
Claim transformations is an advanced feature that allows you to modify a claim value before it is sent to the OIDC relying party. The most common reason to modify a claim is that the service provider requires a claim in a certain format that isn't available from your authentication source. An example is that some relying parties offer sandbox environments but require that the username end in
.sandbox. This isn't something you'd typically have stored in your authentication source so you wouldn't be able to protect that sandbox account using OIDC. Claim transformations solves this problem by allowing you to modify your claims.Claim transformations work by operating on a list of rules from top to bottom to transform a claim into exactly what you need. The attribute selected on the first line is used as the primary attribute to be transformed. All rules after the primary attribute was specified will continue to modify this same attribute. The list of rules can be seen below.
When specifying attributes use the attribute name from your authentication source as shown in the claims for your enabled OIDC scopes for this application, such as the
<Email Address>attribute from theemailclaim in the "Email" OIDC scope. These can be the default attributes from the pre-created claims, or custom attributes you create in your claims.When creating a transformation rule you can use it to create a temporary attribute. Temporary attributes create variables via the transformation language then can be reused for more complex transformations. When you create a temporary attribute and give it a name, you can then specify that temporary attribute by name in subsequent rules.
Each rule should be on its own separate line and go in order from top to bottom of how you'd like the claim transformed.
Rule format is:
$RULE_NAME $OPTION="$OPTION_VALUE"A rule can have more than one option and the option name must always be followed by an
=and the option value encapsulated in quotes.Rule Name Description Options useAlways used as the first rule to define the primary attribute to modify. The attribute name should always be surrounded by quotes.
No options.
prependThis rule allows you to prepend static text or the value of another attribute from your authentication source to the start of your primary attribute.
text: Static text to add to the start of the attribute. Must use this oradditional_attrbut not both.
Example:prepend text="admin-"additional_attr: The name of another authentication source attribute to add to the start of your primary attribute. Must use this ortextbut not both.
Example:prepend additional_attr="sAMAccountName"
appendThis rule allows you to append static text or the value of another attribute from your authentication source to the end of your primary attribute.
text: Static text to add to the end of the attribute. Must use this oradditional_attrbut not both.
Example:append text="@example.com"additional_attr: The name of another authentication source attribute you'd like to add to the end of your primary attribute. Must use this ortextbut not both.
Example:append additional_attr="domain_name"
insert_beforeThis rule allows you to add static text or the value of another attribute from your authentication source before a delimiter that you specify.
delimiter: The character(s) used to identify where to add text before. It can be repeated to allow delimiting by more, logically inclusive, character(s). Required.text: Static text to add before the delimiter. Must use this oradditional_attrbut not both.
Example:insert_before delimiter="@" text="-admin"additional_attr: The name of another authentication source attribute you'd like to added before the delimiter. Must use this ortextbut not both.
Example:insert_before delimiter="@" additional_attr="sAMAccountName"
insert_afterThis rule allows you to add static text or the value of another attribute from your authentication source after a delimiter that you specify.
delimiter: The character(s) used to identify where to add text after. It can be repeated to allow delimiting by more, logically inclusive, character(s). Required.text: Static text to add after the delimiter. Must use this oradditional_attrbut not both.
Example:insert_after delimiter="@" text="example"additional_attr: The name of another authentication source attribute you'd like to added after the delimiter. Must use this ortextbut not both.
Example:insert_after delimiter="@" additional_attr="domain_name"
joinThis rule joins the values of an attribute, which is an array of strings, into a single string separated by a specified separator.
separator: The string used to separate each element in the joined string. Required.
Example:
join separator=","keep_beforeThis rule removes text from your attribute after the delimiter, keeping only what was before it.
delimiter: The character(s) used to identify where to split the text and keep only what was before it. It can be repeated to allow delimiting by more, logically inclusive, character(s). Required.
Example:keep_before delimiter="@"
keep_afterThis rule removes text from your attribute before the delimiter, keeping only what was after it.
delimiter: The character(s) used to identify where to split the text and keep only what was after it. It can be repeated to allow delimiting by more, logically inclusive, character(s). Required.
Example:keep_after delimiter="@"
make_uppercaseUppercases the entire text of the attribute.
No options
make_lowercaseLowercases the entire text of the attribute.
No options
format_ad_groupsThis rule automatically filters Active Directory groups from their LDAP path name to only contain the group names.
filter: When specified, will only return group names that contain the word specified in the filter. You may usefilterorstartswithbut not both. It can be repeated to allow filtering by more, logically inclusive, words. Optional.
Example:format_ad_groups filter="admin"explicit: Can be used with optionfilter. When set totruewill only return a group name that exactly matches the filter name. Optional.
Example:format_ad_groups filter="admin-aws" explicit="true"startswith: When specified, will only return group names that start with the word specified. You may usestartswithorfilterbut not both. It can be repeated to allow filtering by more, logically inclusive, words. Optional.
Example:format_ad_groups startswith="enterprise"ignorecase: Can be used with optionsfilterandstartswith. When set totruewill return all groups that match options with ignored case. For example,format_ad_groups filter="admin" ignorecase="true"will also returnADMINif this group exists. Optional.
removeThis rule allows you to remove the first or all occurrences of static text or the value of another attribute from your authentication source to your primary attribute.
text: Static text to remove from the attribute. Required. Must use this oradditional_attrbut not both.
Example:remove text="@example.com"additional_attr: The name of another authentication source attribute you'd like to remove from your primary attribute. Required. Must use this ortextbut not both
Example:remove additional_attr="domain_name"all: When set to true will remove all occurrences. Optional.
Example:remove text="_" all="true"
Examples
Below are some examples of different scenarios and how you can transform the claims to solve your problem.
Example 1
A relying party requires that all your email addresses end in
.sandboxbut you don't have an attribute in your authentication source that does.You have an email attribute named
mailand your user's email isjdoe@example.com.use "mail" append text=".sandbox"- Line 1 picks the mail attribute from your authentication source to use for all rules below it. The example user's
mailattribute value isjdoe@example.com. - Line 2 appends the static text value specified to the end of the
mailattribute. This changes the example value tojdoe@example.com.sandbox
Example 2
You need to change the domain of an email address attribute to be from
acme.corptoexample.com.You have an email attribute named
mailand your user's email isjdoe@acme.corp.use "<Email Address>" keep_before delimiter="@" append text="@example.com"- Line 1 picks the mail attribute from your authentication source to use for all rules below it. The example user's
mailattribute value isjdoe@acme.corp. - Line 2 keeps only the text before the delimiter character
@. This changes the example value tojdoe. - Line 3 appends the text value to the end of the
mailattribute's value. This changes the example value tojdoe@example.com.
Example 3
You want to create an attribute that has a "no-reply" email address for a department, but no such attribute value exists in your identity store.
You have a custom
departmentattribute that contains department names, and your email domain isexample.com.First, create a temporary attribute rule with the temporary attribute name set to
noreply_prefix:use "department" append text="-no-reply"- Line 1 picks the
departmentattribute from your authentication source, with an example value ofsales. - Line 2 appends the text value
-no-replyto the end of thedepartmentattributes value, resulting in the temporary attributenoreply_prefixwith the valuesales-no-reply.
Next, create a normal transformation rule to create the claim using the resulting email address via transformation:
use "noreply_prefix" append text="@example.com"- Line 1 uses the
noreply_prefixattribute created by the temporary attribute transformation rule preceding this rule in the stack. - Line 2 appends the email domain
example.comto the temporary attribute's value, resulting in the email addresssales-no-reply@example.com
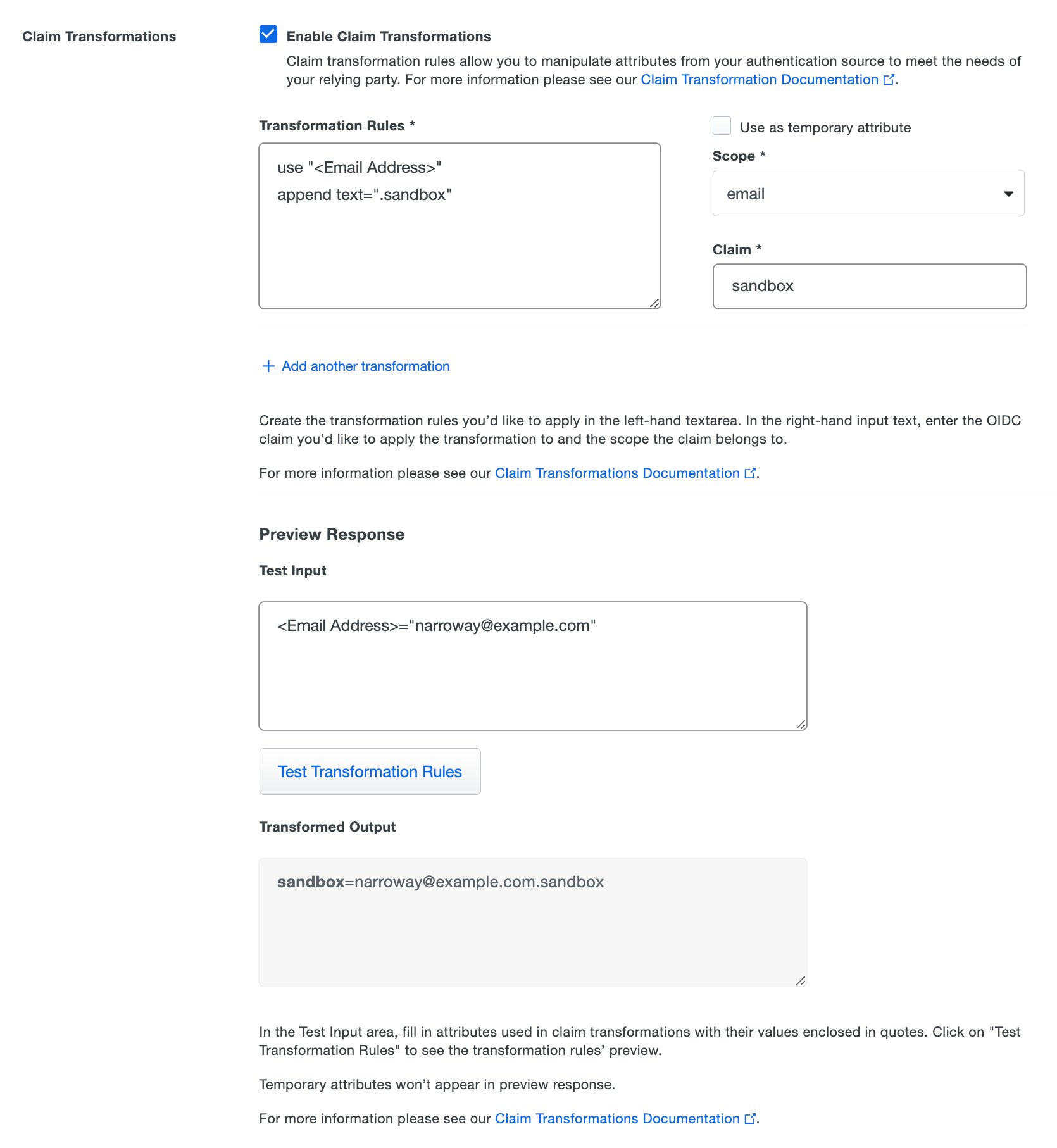
How to enable claim transformations
-
Next to Claim Transformations check the box for Enable Claim Transformations. New options will appear below.
-
On the left-hand side under Transformation Rules you can use the rules above to fill out the textbox with how you'd like to transform a claim.
-
If you want to use this rule to create a temporary attribute, select the Use as temporary attribute option on the right-side of the rules editor, and specify the name you want to use for the resulting attribute in the Temporary Attribute Name box.
-
If not creating a temporary attribute, then on the right-hand side you select a scope this transformed claim will be mapped to from the Scope drop-down.
-
Under Claim type in the new claim name you want sent to your relying party.
-
If you'd like to add additional attributes to transform click Add another transformation.
Preview Response
Use the "Preview Response" tool to test the outcome of your transformation rules and see what will be sent in the OIDC response.
-
Provide values for attributes used in transformations in the Test Input box. Enclose attribute values in quotes.
If you're transforming AD groups, you will need to enclose the AD group values in quotes and separate multiple groups with commas.
-
After you specify all values for attributes used in transformation rules, click Test Transformation Rules. If all transformation rules are correct, the "Transformed Output" section shows the transformed attributes with rules applied.
Validation errors for any transformation rules will be shown underneath the "Test Input" area. If any of the test input values provided are incorrect, you will see an error message describing which provided attributes are incorrect. Correct the transformation rule or test input information and try the test again.
Duo Universal Prompt
The Duo Universal Prompt provides a simplified and accessible Duo login experience for web-based applications, offering a redesigned visual interface with security and usability enhancements.
Universal Prompt Traditional Prompt 
We've already updated the Duo generic OIDC relying party application hosted in Duo's service to support the Universal Prompt, so there's no action required on your part to update the application itself. If you created your generic OIDC relying party application before March 2024, you can activate the Universal Prompt experience for users from the Duo Admin Panel. generic OIDC relying party applications created after March 2024 have the Universal Prompt activated by default.
If you created your generic OIDC relying party application before March 2024, it's a good idea to read the Universal Prompt Update Guide for more information, about the update process and the new login experience for users, before you activate the Universal Prompt for your application.
Activate Universal Prompt
Activation of the Universal Prompt is a per-application change. Activating it for one application does not change the login experience for your other Duo applications.
The "Universal Prompt" area of the application details page shows that this application is "Ready to activate", with these activation control options:
- Show traditional prompt: Your users experience Duo's traditional prompt via redirect when logging in to this application.
- Show new Universal Prompt: (Default) Your users experience the Universal Prompt via redirect when logging in to this application.
The application's Universal Prompt status shows "Activation complete" here and on the Universal Prompt Update Progress report.
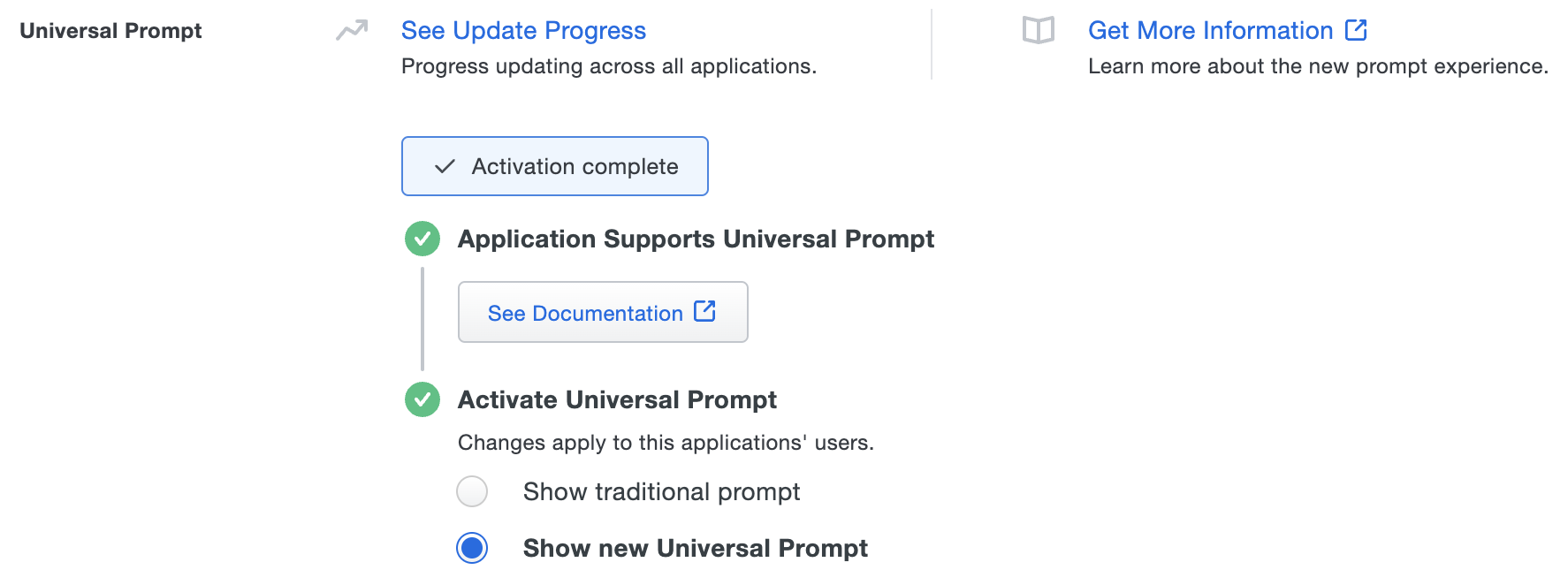
Should you ever want to roll back to the traditional prompt, you can return to this setting and change it back to Show traditional prompt. However, this will still deliver the Duo prompt via redirect, not in an iframe. Keep in mind that support for the traditional Duo prompt ended for the majority of applications in March 2024.
Universal Update Progress
Click the See Update Progress link to view the Universal Prompt Update Progress report. This report shows the update availability and migration progress for all your Duo applications. You can also activate the new prompt experience for multiple supported applications from the report page instead of visiting the individual details pages for each application.
Verify SSO
You can log into most applications using SSO by visiting their website directly.
You can log into your application using Duo Central, our cloud-hosted portal which allows users to access all of their applications in one spot. You can add your OIDC applications to Duo Central by following the Add Application Tiles section of the page either entering in the base URL for the application you'd like users to access or provide an RP-initiated login URL if provided by the relying party.
When you log into an application provided by Duo's Single Sign-On, you will be redirected to Duo Single Sign-On to begin authentication.
Duo-hosted or Active Directory Login
With Duo or Active Directory as the Duo SSO authentication source, enter the primary username (email address) on the Duo SSO login page and click or tap Next.
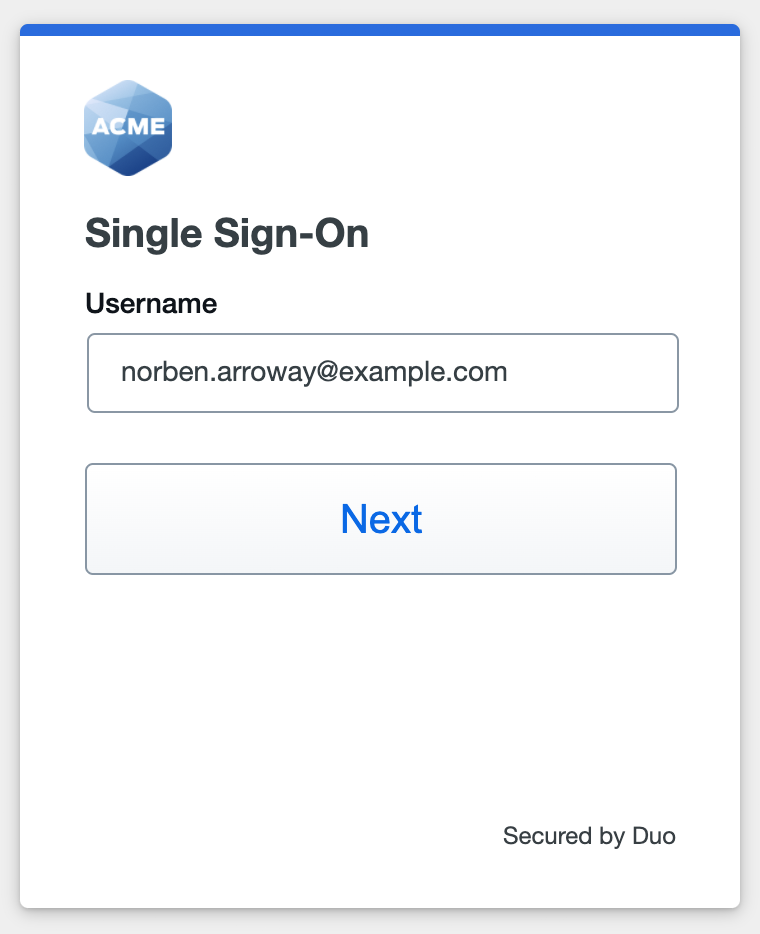
Enter the Duo or AD primary password and click or tap Log in to continue.
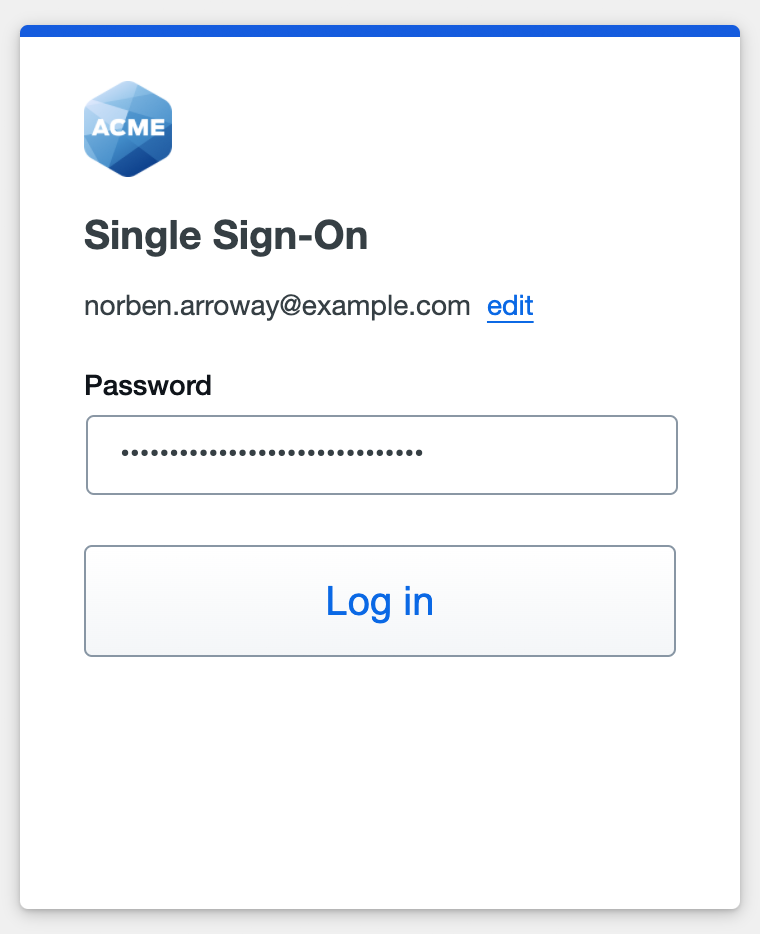
When using Duo Passwordless you won't need to enter a password, and will proceed directly to Duo authentication.
SAML Login
With a SAML identity provider as the Duo SSO authentication source, Duo SSO immediately redirects the login attempt to that SAML IdP for primary authentication. Users do not see the Duo SSO primary login screen.
Duo Authentication
Successful verification of your primary credentials by Duo, Active Directory, or a SAML IdP redirects back to Duo. Complete Duo two-factor authentication when prompted and then get redirected back to the relying party application to complete the login process.
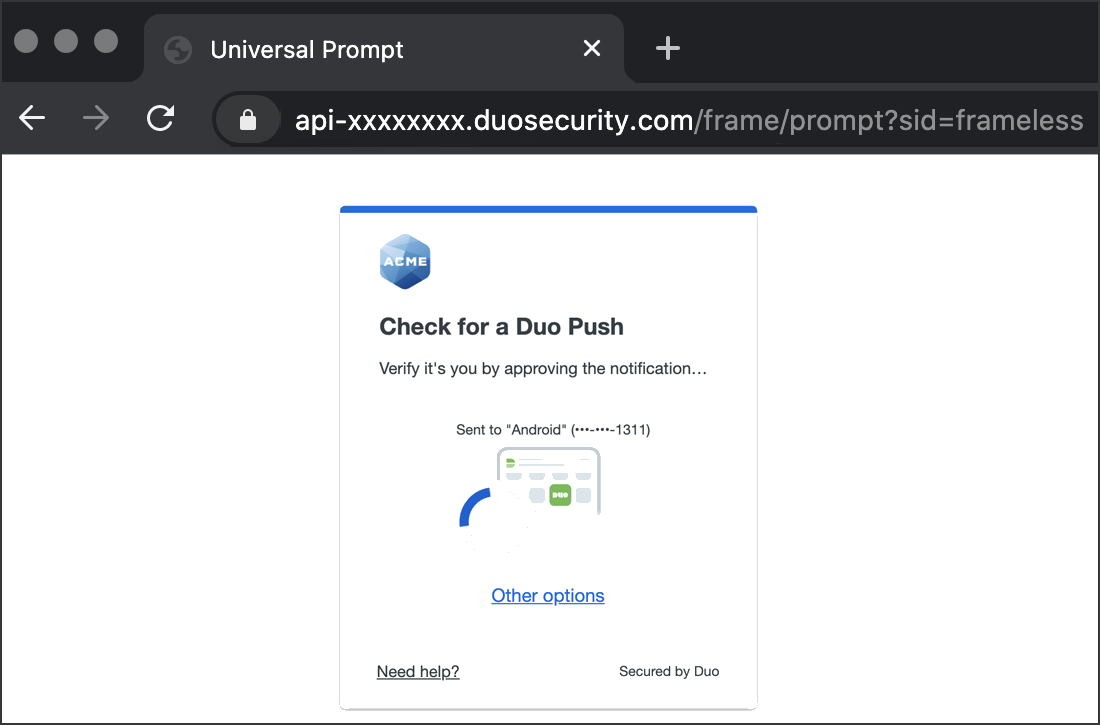
*Universal Prompt experience shown.
Grant Access to Users
If you did not already grant user access to the Duo users you want to use this application be sure to do that before inviting or requiring them to log in with Duo.
Enable Remembered Devices
To minimize additional Duo two-factor prompts when switching between your relying party application and your other Duo Single Sign-On SAML applications, be sure to apply a shared "Remembered Devices" policy to your SAML applications.
OpenID Request Examples
Certain OpenID endpoints used throughout the authentication flow may require the Relying Party to make requests with specific data to the endpoint. The below information will highlight each endpoint with its specific requirements and an example of the request to/and response from our service.
All URLs start with the Issuer under the Metadata section. Example URLs will be used below.
Discovery URL
Unauthenticated metadata endpoint that returns configuration information about the authorization server including which grant types and scopes are configured.
GET /.well-known/openid-configurationExample Response
{ "issuer":"https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567", "authorization_endpoint":"https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567/authorize", "token_endpoint":"https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567/token", "jwks_uri":"https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567/jwks", "response_types_supported":[ "code" ], "subject_types_supported":[ "public" ], "id_token_signing_alg_values_supported":[ "RS256" ], "introspection_endpoint":"https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567/token_introspection", "userinfo_endpoint":"https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567/userinfo", "scopes_supported":[ "openid", "email", "profile" ], "response_modes_supported":[ "query", "fragment" ], "grant_types_supported":[ "authorization_code" ], "token_endpoint_auth_methods_supported":[ "client_secret_basic", "client_secret_post", ], "introspection_endpoint_auth_methods_supported":[ "client_secret_basic", "client_secret_post" ], "code_challenge_methods_supported":[ "S256" ] }JWKS URL
Unauthenticated endpoint that returns JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) information about the authorization server that can be used to validate signatures signed by the server.
GET /jwksExample Response
{ "keys":[ { "kty":"RSA", "use":"sig", "alg":"RS256", "kid":"6f1636b67f198fc9c594cbbd85d406d145c50db0869e92f03d4c864c2e35b9aa", "n":"vkDLxi_fCM9mhWY2z_im85BcCepwOKyCPDQSvHXRv-PN2k0TawS-yQrZPScMsIOFkSnLEY1k7BRUrXK0YVsLPUFgyoKWQnXltsmWL06XNeFwTzZs67HgWgIA3CaIa9Ph8gbtpvBayjsc_CuHCts25-sJEheFw1teioJBDJFPC18ZwniKC8cbkoWBrf1y0FEHXlGmsaAXY7uGdfPQWw2GCfnQds9YwIRre_KFkwvhC9xhJ_syMSd0TEaZSJXUflN3Vph8MEjkZ12AzIeb-1wV1PULVIReKFubTOVL1mOvL_X9qmtU3b004BbIyKUY5gSEDSKAHfULj0jXgdazmUavrW3kmza9LYCpNgNDFJH1y6J90HV2t8E3dFRRLXHVsnF7ImcQuH2gX_kVL5jP0KH3FcmKtDf0uoiVX7dHC0ohWyRemROVkjgmJYvds4mVKjaulwICltk9GSH0Fe9x13fy9R668KzpFDbtIZdrAa2cztFggQKTKjgEStKfctlC-yS2jMGATUI96XOKK0ZPo0Bf8xB5cEOsdGSREcMXVk4PcrfUAzeFTkA2JlruYQ42JyCvEEVfvxelxyJlB8iplelZJGCEnJday_ilywCJWPYqiuMWzl5ctKdzRdY823ZyzlNLv5jGKlpfd8iywD6JkO578nmrjSVx9yI9KwbQJWD-Yos", "e":"AQAB" }, { "kty":"RSA", "use":"sig", "alg":"RS256", "kid":"5a23604dc51e1c568c43d0294cce1e7a0fd496d20ba55531d48b8dccbe21aa30", "n":"7PGr5CD-FWKTKbOQqOM964-AhwIpfhmrCf2u7L_HF_ZDM3eyP__KGAePdhMCDcMrQbCFWpXURDN8KnpDmuM5sMRn2j3QDM4YyabWb4MbIlc0OvHYNf113EKwb_VxphUFkmPAwF4X73uxeIv12ZSrz7rgMi-Ujj7dZwl6JaZvpzyFE8wLKw_MJ__sgME6-dp1zvGitepMJURPZDNph767gcA-Gw08snFJXCOdv8SyXKvVQkrxtzNzT8PWKwjeIVQW0LNySMj7nj93ruIOAjqk9WGJO5_CYobBl-QDC15BMK_capjgMEWLHlulrnL9Xsws_SixmcZqtK40AdmD1OIYcHNbXbLc0ELVip0ibvsqr1bh9lyFvyHJ0HVf_5jIUGBNndFq0NHoraRSFxCJ1l9_riYLGBsMaLFucqsqjeh_DV81hvsfJXYVom0gvdAjKA6e4QxQdc1GF0YIc4S5ojElo3S1350x_SKhwmufkQ6dcshHHT8DJSijdLRMtCLVzpQbhQpFA0QgUfTYpAScrAu59LsedYitmobWKTkq9VQcz5lHPDSudcpKOi9EjUR2UgpRDFyrG09Bi01ax6tT6RFfut-0_EOwAndIMn3Gm9cnnInpIG-eMbYMZmu0tFHFfOknQYISt1qUWyVOItOzlVKxMkF5wZ3WygCz8xRZ7wsmVDM", "e":"AQAB" } ] }Authorize URL
URL to start a new authentication usually redirected here from the relying party. Once the request is sent the user will be asked to authenticate through Duo Single Sign-On. Upon successful authentication they will be redirected back to the relying party with information.
GET /authorizeParameters
Below is the information that you'll need to complete a Authorize URL request.
Parameter Required? Description client_idRequired The client ID for the application found in the Metadata section of the application's Duo Admin Panel. Example:
DIABC123678901234567response_typeRequired Authorization Code Flow is the only supported response type so the value
codeshould be sent.redirect_uriRequired The URI making the request. This must match one of the redirect URIs defined for the relying party in the Duo Admin Panel.
scopeRequired A space separated list of requested scopes for the authentication. Example:
openid email profile.nonceRecommended A value that will be returned in the ID token as a way to mitigate replay attacks.
code_challengeOptional* A challenge for PKCE that will relate to a
code_verifierthat will be sent when redeeming the authorization_code on the token endpoint. If this value is sent in an authorization request than the correspondingcode_verifiermust be presented on the token call or an error will be returned.code_challenge_methodOptional* If
code_verifieris sent in the authorization request a value ofS256must be sent for this field.login_hintOptional The email address of the user from the relying party that can be used to automatically fill in the Email Address field on the SSO login page.
promptOptional Options to prompt users for reauthentication. Options:
none,login.response_modeOptional The way the authorization response is returned to the relying party. Options:
query,fragmentDefault:query.stateOptional A value that will be returned in the response. Relying parties can use this remember state of a request.
Authorization Request Format
curl --get "https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567/authorize" \ --data-urlencode "client_id=$clientId" \ --data-urlencode "response_type=code" \ --data-urlencode "redirect_uri=$redirectUri \ --data-urlencode "scope=openid email profile" \ --data-urlencode "state=hb98d207c5"Authorization Request Example Response
Upon successful authentication the user will be redirected back to the relying party with a
codeneeded to retrieve the tokens. Thestateparameter might also be sent if the initial request contained it.$redirectUri?code=xeojklgvbcri998e4g8m&state=hb98d207c5Token URL
URL used by the relying party to retrieve the access, id, and refresh tokens after a user has successfully authenticated to the authorization server and has returned to the relying party with an auth code. This endpoint can also be used to submit refresh tokens to get new access, id, and refresh tokens without requiring the user to do another interactive login.
POST /tokenParameters
Below is the information that you'll need to complete a Token URL request.
Parameter Required? Description client_idRequired The client ID for the application found in the Metadata section of the application's Duo Admin Panel. Example:
DIABC123678901234567client_secretRequired The Client Secret for the application found in the Metadata section of the application's Duo Admin Panel. Example:
wXyI4DMSD34kuJAKMaD2JAr2UzFo9iVey6a8ff5h.grant_typeRequired Requires the value
authorization_codeorrefresh_token.codeRequired* Only required if
grant_typeofauthorization_codeis used. The value that was returned from the authorization request.refresh_tokenRequired* Only required if
grant_typeofrefresh_tokenis used. The value that was returned from the refresh token request.redirect_uriRequired The redirect uri that was used in the authorization request.
code_verifierOptional Code that validates the code_challenge sent in during the authorize endpoint to satisfy Proof Key for Code Exchange.
Token Request Format
curl -v -X POST \ -H "Content-type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \ "https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567/token" \ -d "client_id=$clientId" \ -d "client_secret=$clientSecret" \ -d "grant_type=authorization_code" \ -d "redirect_uri=$redirectUri" \ -d "code=$code"Token Request Example Response
"access_token": "eyJraWQiOiAiNmYxNjM2YjY3ZjE5OGZjOWM1OTRjYmJkODVkNDA2ZDE0NWM1MGRiMDg2OWU5MmYwM2Q0Yzg2NGMyZTM1YjlhYSIsICJhbGciOiAiUlMyNTYiLCAidHlwIjogImp3dCJ9.eyJpc3MiOiAiaHR0cHM6Ly9zc28tYWJjMWRlZjIuc3NvLmR1b3NlY3VyaXR5LmNvbS9vaWRjL0RJQUJDMTIzNjc4OTAxMjM0NTY3IiwgInN1YiI6ICJiMWNlZTRlNTVkZWM1YTY2NTU0NmFkZGE4ZWQxYmViMjlkMDdlYzJjOTkyMjE0MzhjZWRmZDYzYzUwZGI1OTQ1IiwgImF1ZCI6ICJESUFCQzEyMzY3ODkwMTIzNDU2NyIsICJleHAiOiAxNjgxMTM4MzcxLCAiaWF0IjogMTY4MTEzNDc3MSwgInNjb3BlIjogImVtYWlsIHByb2ZpbGUgb3BlbmlkIn0.IGNxpZbPjQW6RVzf9r35nVMWRH_TGTLgmvY6yLguZRuGvYuX1PtRpqzHl7iN69TfSzlRqHRj5SVrH4tN8R_73W0pLppNObCHCnNBgsCMsp8KRidihtHANwHuXe-E501WJ5aPaDwypmwIR6PH-p0fSCHFuldNFOUGO9J21p6FGzBPx_rjVm9zImtinxTLD4DP1_EoSCfjGqFHk7dLvpUmURb9hb3VJeP0pS1TP3AjVYzgGG3ChDioh1GLedoj9ICdxZ2SjY6oVZgh9R9-d9t2CzTif0xdl1Rv0OMU-rEH_qesAYvCQMRvXSSF-wET502DLivvj3d5MADO947g2garm1I9DSrV1nWFYugKC8HvrsbEwwD-EHTE8KaGbqPhixFJIFIQiVpqYb6Ro87wBT4zpycdV6IA56xYOFw6SAsPGXq-kCKf0ljeEPt9Gvq5ioyQ53V57a3J8xl12x7NsflAwOIBdgk-Y61YNnY0fWMfQJKf-z1NW9OCfXtzkBIZhDF7xpmOebPVmZECl03hM5hc8Yewku3QEWsXAepbBWUEsPmO0Bg5Yrf02IX6x2hW-vGDFT8YbjYlDsqF-CjHr3hWSSlDl0YvhYtMyHO5SSux300vHfg1URyHPsnpREp5JOyX0JFMoPv8Ar4NmzSn1znIawvp31bhZ0Idatw02olLDWE", "token_type": "Bearer", "expires_in": 3600, "id_token": "eyJraWQiOiAiNmYxNjM2YjY3ZjE5OGZjOWM1OTRjYmJkODVkNDA2ZDE0NWM1MGRiMDg2OWU5MmYwM2Q0Yzg2NGMyZTM1YjlhYSIsICJhbGciOiAiUlMyNTYiLCAidHlwIjogImp3dCJ9.eyJlbWFpbCI6ICJ0ZXN0QGV4YW1wbGUuY29tIiwgIm5hbWUiOiAiVGVzdCBVc2VyIiwgImdpdmVuX25hbWUiOiAiVGVzdCIsICJmYW1pbHlfbmFtZSI6ICJVc2VyIiwgImlzcyI6ICJodHRwczovL3Nzby1hYmMxZGVmMi5zc28uZHVvc2VjdXJpdHkuY29tL29pZGMvRElBQkMxMjM2Nzg5MDEyMzQ1NjciLCAic3ViIjogImIxY2VlNGU1NWRlYzVhNjY1NTQ2YWRkYThlZDFiZWIyOWQwN2VjMmM5OTIyMTQzOGNlZGZkNjNjNTBkYjU5NDUiLCAiYXVkIjogIkRJQUJDMTIzNjc4OTAxMjM0NTY3IiwgImV4cCI6IDE2ODExMzUwNzEsICJpYXQiOiAxNjgxMTM0NzcxLCAibm9uY2UiOiAiQUJDMTIzIiwgImF0X2hhc2giOiAiaXFqWTllR3JzemZtYjhXcVU1RTNWZyIsICJhdXRoX3RpbWUiOiAxNjgxMTM0NzYxfQ.uFDOvGw-K4GlKiOV6p2j22LOWqTIlGqtWG1NZkyrsxXnzve-wl_xundfLALytmc-lsdmHOwYsMy-QfEvrFhqoFR4AGDE-La_inTdSQob-hSsf-UX8yhu4JnY4X-6a6i556sGvhpnV9j27iWgJYKdibAsY5BAyY2pgmpLV3CDf6T5yoyaQv2CqbFDaAtEz76_9SjDaW1rqKoyYlIrJHiAAGiUL845LYpC2WOr5jjLZAOonPNtJreQwR9oAqU0MK362lxjnyswP4H7eTJwe9SvHHyTM4Z237QBXXUY7FIGzqESXSVX3K3EmCDOcktO9VrhOwdiBy_OsCtdaJshFAhlk3m9VL_q1pAfUJKO81McEwz7EMYzG8X6qRTheZXDaFdkzw8naR7pGTgkJ0xezVVCvqzym1TF6h1CmJDApkRqZ4XEJQD09j7F4-D1eiEJM-rCD7lJz2Mw00AOJlqzaLbKfjPtMXorr40bK5kIy5ikVv-Jop4PtXxSNejIf0nLCy2jBPi_SN_IIJVbYvFU70LbgI0CR-b6BjsfyoiotF7q3KnGXNVDEdGO_Bv9-WHdkyMFAB88gCyuNfwzLEyNA2f6F0cg3ulUa0UMc-p-uXFVSDrYrbV_eAsVKtLS1c2CbRbkWymbCBn3z7XnXKXC4ei3UZs3ZgjChZqxx44-OyiF9S8"Token Introspection URL
URL takes an access token or refresh token and provides information about the token including if it is still active, which scopes it has access to, and when the token expires.
POST/token_introspectionParameters
Below is the information that you'll need to complete a Token URL request.
Parameter Required? Description client_idRequired The client ID for the application found in the Metadata section of the application's Duo Admin Panel. Example:
DIABC123678901234567.client_secretRequired The client secret for the application found in the Metadata section of the application's Duo Admin Panel. Example:
wXyI4DMSD34kuJAKMaD2JAr2UzFo9iVey6a8ff5h.tokenRequired The access or refresh token that will be inspected. This should be presented in the same format that it was retrieved from the /token endpoint earlier.
token_type_hintOptional Can be either
access_tokenorrefresh_tokento help determine which type of token to look up.Token Introspection Request Format
The client ID and client secret separated by a
:must be base64 encoded before being sent. The example below does this but may not work on all systems.curl -v -X POST \ -H "Content-type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \ -H "Authorization: Basic $(echo -n "$clientId:$clientSecret"| base64)" \ "https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567/token_introspection" \ -d "token=eyJpc3MiOiAiaHR0cHM6Ly9zc28tYWJjMWRlZjIuc3NvLmR1b3NlY3VyaXR5LmNvbS9vaWRjL0RJQUJDMTIzNjc4OTAxMjM0NTY3IiwgInN1YiI6ICJiMWNlZTRlNTVkZWM1YTY2NTU0NmFkZGE4ZWQxYmViMjlkMDdlYzJjOTkyMjE0MzhjZWRmZDYzYzUwZGI1OTQ1IiwgImF1ZCI6ICJESUFCQzEyMzY3ODkwMTIzNDU2NyIsICJleHAiOiAxNjgxMTM4MzcxLCAiaWF0IjogMTY4MTEzNDc3MSwgInNjb3BlIjogImVtYWlsIHByb2ZpbGUgb3BlbmlkIn0"Token Request Introspection Example Response
{ "active": true, "scope": "profile email openid", "client_id": "DIABC123678901234567", "username": "test@example.com", "token_type": "access_token", "exp": 1681138371, "iat": 1681134771, "nbf": 1681134771, "sub": "b1cee4e55dec5a665546adda8ed1beb29d07ec2c99221438cedfd63c50db5945", "iss": "https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567" }User Info URL
URL takes an access token and provides information about the user.
GET/userinfoParameters
Below is the information that you'll need to complete a Token URL request.
Parameter Required? Description tokenRequired The access token related to the user. This should be presented in the same format that it was retrieved from the /token endpoint earlier.
User Info Request Format
curl -v -X GET \ -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJpc3MiOiAiaHR0cHM6Ly9zc28tYWJjMWRlZjIuc3NvLmR1b3NlY3VyaXR5LmNvbS9vaWRjL0RJQUJDMTIzNjc4OTAxMjM0NTY3IiwgInN1YiI6ICJiMWNlZTRlNTVkZWM1YTY2NTU0NmFkZGE4ZWQxYmViMjlkMDdlYzJjOTkyMjE0MzhjZWRmZDYzYzUwZGI1OTQ1IiwgImF1ZCI6ICJESUFCQzEyMzY3ODkwMTIzNDU2NyIsICJleHAiOiAxNjgxMTM4MzcxLCAiaWF0IjogMTY4MTEzNDc3MSwgInNjb3BlIjogImVtYWlsIHByb2ZpbGUgb3BlbmlkIn0" \ "https://sso-abc1def2.sso.duosecurity.com/oidc/DIABC123678901234567/userinfo"Token User Info Example Response
{ "name": "Test User", "given_name": "Test", "family_name": "User", "email": "test@example.com", "sub": "b1cee4e55dec5a665546adda8ed1beb29d07ec2c99221438cedfd63c50db5945", "user": "test@example.com" }Automated Provisioning
You may be able to create, manage, and delete users and groups in this application automatically from Duo using SCIM 2.0 provisioning. See Automated Provisioning to learn how.
Troubleshooting
Need some help? Try searching our Knowledge Base articles or Community discussions. For further assistance, contact Support.
